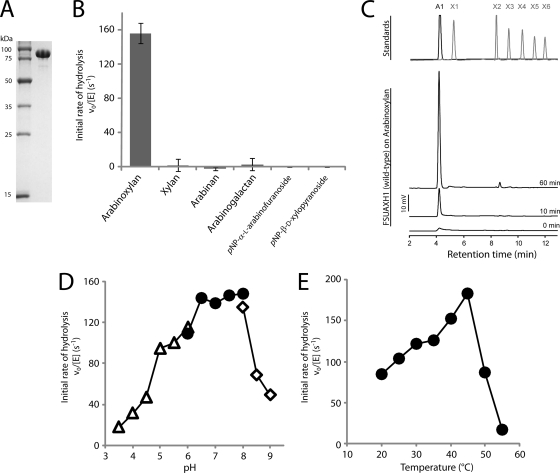
FIG. 1.
FSUAXH1 (FSU2269) catalyzes the cleavage of arabinose moieties from arabinoxylan. (A) SDS-PAGE showing purified recombinant FSUAXH1 wild-type protein. The protein was purified as described in Materials and Methods, and 2.5 μg of protein was loaded on a 12.5% polyacrylamide gel and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue G-250. (B) Catalytic activities of FSUAXH1. Substrates in sodium phosphate buffer were incubated with FSUAXH1, and the initial catalytic rates were determined. Bars are shown with standard errors for three independent experiments. (C) Time course of cleavage of arabinose from arabinoxylan by FSUAXH1. Arabinoxylan (0.5% [wt/vol]) in sodium phosphate buffer was incubated with 5 nM FSUAXH1 for 0, 10, and 60 min, and the products of hydrolysis were analyzed by HPAEC/PAD. Standards of arabinose (A1), xylose (X1), and xylooligosaccharides (X2 to X6) were resolved under the same conditions, and the retention times are shown in the upper panel. (D) Effect of pH on hydrolysis of arabinoxylan by FSUAXH1. Reactions were carried out at 39°C in 50 mM citrate-NaOH (open triangles; pH 3.5 to 6.0), 50 mM Na2HPO4-HCl (closed circles; pH 6.0 to 8.0), and bicine-NaOH (open diamonds; pH 8.0 to 9.0). (E) Effect of temperature on hydrolysis of arabinoxylan by FSUAXH1. Reactions were performed in 50 mM Na2HPO4-HCl (pH 7.5) and 100 mM NaCl buffer at temperatures ranging from 20°C to 55°C.