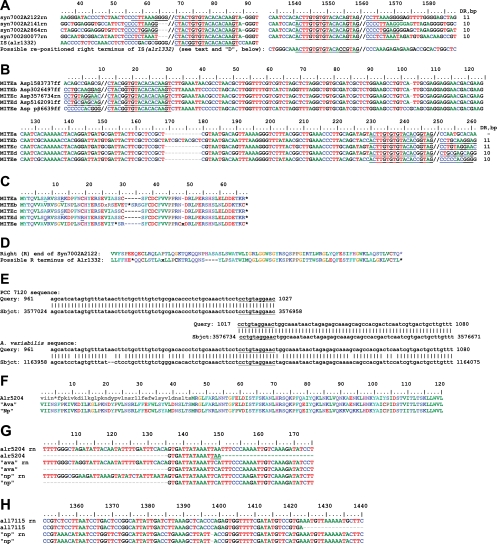
FIG. 2.
Transposable elements in the IS4 family. Border regions of IS(alr1332) and related ISs from Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7002 (A) and MITEs whose ends are similar to those of the ISs in panel A are shown (B). //, presumptive ends of ISs and MITEs; rn, region. The Syn7002 ISs extend from position 71 to position 1559, the MITEs extend from position 853 to 1559, and IS(alr1332) extends from position 71 to, possibly, the end of MITE Asp1583737 at position 1559. (C) When frameshifts (x) and stop codons (*) are considered, the amino acid sequences of the MITEs appear very similar. (D) Predicted product of translation of what may be a repositioned fragment of the 3′-terminal portion of alr1332, compared with the predicted 3′-terminal product of Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7002 ORF A2122. (E) BLASTn analysis using, as query, the “pretransposition” sequence of Anabaena sp. in the vicinity of MITEc. With Anabaena sp. as subject, one sees—spaced 224 bp apart—the two copies of the MITE's DR (underlined), whereas with A. variabilis as subject, one sees the unbroken region with the “empty site” without the MITE. (F to H) Single-base pair changes greatly affect the transposase amino acid sequence. (F) Alr5204 is truncated (the black, lowercase amino acid sequence lacks an in-frame start codon) compared with orthologs from A. variabilis (Ava) and N. punctiforme (Np). These proteins and their genes, ava and np, are specified in Fig. S1, clusters 2 (for F and G) and 3 (for H), in the supplemental material. (G) Nucleotide sequence comparison of alr5204 and its orthologs shows that a single nucleotide substitution leads to creation of the stop codon shown in panel F. (H) The C-terminal truncation of all7115, relative to np, results from an indel mutation at position 1398 that leads soon to a termination codon. Numbering of positions here and in other figures is consistent with that used in corresponding supplemental figures.