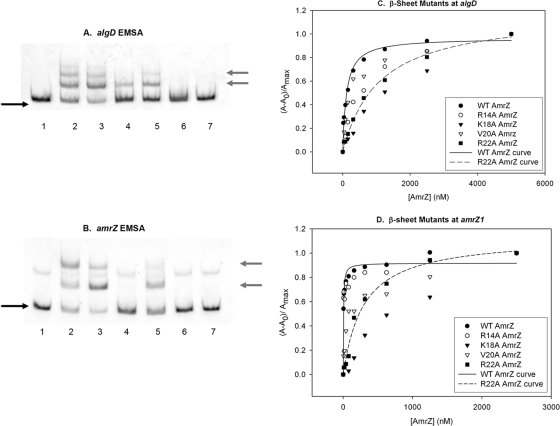
FIG. 4.
Mutation of specific residues causes a loss of AmrZ-mediated DNA-binding activity. (A and B) Protein activity was analyzed with 5′-FAM-labeled PCR-amplified targets of the algD activator (A) or amrZ (B) promoter region. Lanes 1 and 7 have no protein. Lane 2, wild-type AmrZ; lane 3, R14A AmrZ; lane 4, K18A AmrZ; lane 5, V20A AmrZ; lane 6, R22A AmrZ (at 125 nM each). The black arrows on the left indicate free unbound DNA, while the gray arrows indicate the migration of DNA-protein complexes. The fluorescence anisotropy data (see Materials and Methods) were assembled into a table, separated for each target site (Table 1). (C and D) A representative experiment is illustrated for the activator site algD (C) and the high-affinity repressor site amrZ1 (D).