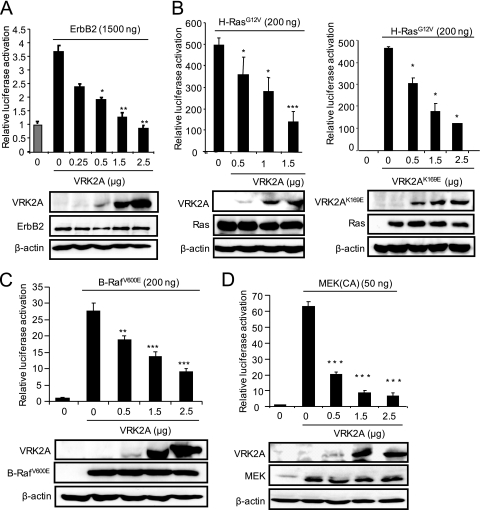
FIG. 2.
VRK2A inhibits the transcriptional response to overexpression of oncogenic ErbB2, H-Ras(G12V), B-Raf(V600E), and MEK1 in MCF7 cells. (A) Effect of VRK2A on the response to ErbB2. Breast carcinoma MCF7 cells were transfected with a fixed amount of ErbB2 and increasing amounts of pCEFL-HA-VRK2A. At the bottom are immunoblots showing the expression of ErbB2 and VRK2A. The experiments to select the amount of ErbB2 to be used and to determine the effects of increasing amounts of VRK2 in HEK293T cells are shown in Fig. S3A and B in the supplemental material. The error bars indicate standard deviations. (B) Effect of VRK2A (left) or VRK2A(K169E) (right) on the SRE transcriptional response to H-Ras(G12V). MCF7 cells were transfected with a fixed amount of H-Ras(G12V) and increasing amounts of pCEFL-HA-VRK2A or pCEFL-HA-VRK2AK169E. At the bottom is shown the expression of VRK2A proteins by immunoblotting with an anti-HA antibody. The experiments to select the amount of H-Ras(G12V) to be used and to determine the effect of increasing amounts of VRK2 in HEK293T cells are shown in Fig. S3C and D in the supplemental material. (C) Effect of VRK2A on the response to B-Raf(V600E). MCF7 cells were transfected with a fixed amount of B-Raf(V600E) and increasing amounts of pCEFL-HA-VRK2A, as indicated. At the bottom is shown an immunoblot determining the expression of B-Raf(V600E) and VRK2A. (D) Effect of VRK2A overexpression on constitutively active MEK (CA) activation of the SRE. Plasmid pFC-MEK1, expressing constitutively active MEK1(S218/222E, Δ32-51), was transfected in the presence of different amounts of VRK2A. The control (0) had the maximum amount of empty vector. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.