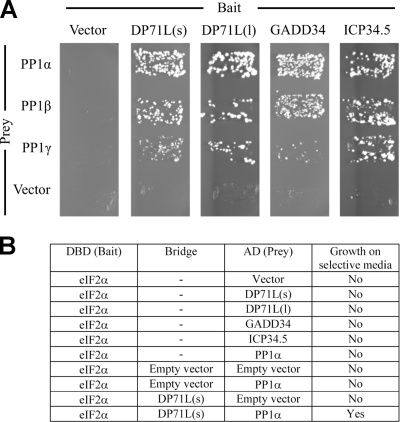
FIG. 4.
DP71L(s), DP71L(l), GADD34, and HSV-1 ICP34.5 interact directly with the α, β, and γ isoforms of PP1, and DP71L(s) can recruit PP1α to eIF2α. (A) Plasmids expressing either DP71L(s), DP71L(l), GADD34, or HSV-1 ICP34.5 fused to the DNA binding domain of the yeast GAL4 protein (bait) were cotransformed into yeast with a plasmid expressing the indicated isoform of human PP1 (prey) fused to the GAL4 activation domain. Vectors expressing unfused GAL4 domains were included as negative controls. Primary transformants were selected on SD-LW (data not shown) and then streaked onto synthetic medium that also lacked histidine (SD-LWH) and contained 5 mM 3-aminotriazole to enhance stringency. Growth on this medium is indicative of protein-protein interaction. (B) A plasmid expressing eIF2α fused to the DNA binding domain of the yeast GAL4 protein (bait) was cotransformed into yeast with a plasmid expressing the indicated prey [DP71L(s), DP71L(l), GADD34, HSV-1 ICP34.5, or the α-isoform of human PP1]. Positive transformants were selected on SD-LW and then streaked onto SD-LWH with 5 mM 3-aminotriazole selective medium to assay for interactions. To study the ability of DP71L(s) to bridge an interaction between eIF2α and PP1, DP71L(s) was expressed as a nucleus-targeted nonfusion protein in cells also expressing eIF2α bait and PP1α prey; triple transformants were initially selected on SD-LWU and then streaked onto SD-LWUH with 5 mM 3-aminotriazole selective medium to assay for interactions.