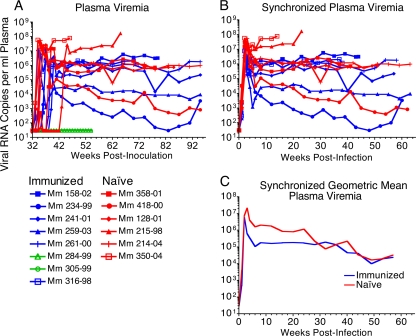
FIG. 8.
Postchallenge plasma viral RNA loads. Viral loads were measured at weekly intervals beginning on week 32 using a real-time RT-PCR assay with a limit of detection of 30 copies of RNA per ml of plasma for the immunized animals that became infected (blue) or remained uninfected (green) and for the naïve controls (red) (A) (19). Viral load measurements were synchronized to the last week in which viral RNA was undetectable in each animal that became infected (B). Comparison of geometric mean viral loads for the infected animals revealed acute peak viremia was reduced by 0.72 log (P = 0.0038; two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test) and was lower by 1.1, 1.2, 1.1, and 1.0 log on weeks 4, 6, 8, and 12 in the immunized group (C). Set point viral loads were significantly reduced for the period between weeks 5 and 67 postinfection, centered on week 28, as determined by a mixed linear model analysis (P = 0.004; 0.96 log lower; 95% CI, 0.31 to 1.6). Due to progression to AIDS, naïve control animals Mm 230-04, Mm 215-98, Mm 358-01, and Mm 128-01 were euthanized weeks 16, 23, 43, and 51 postinfection, and immunized animals Mm 316-98 and Mm 158-02 were euthanized 38 and 44 weeks postinfection.