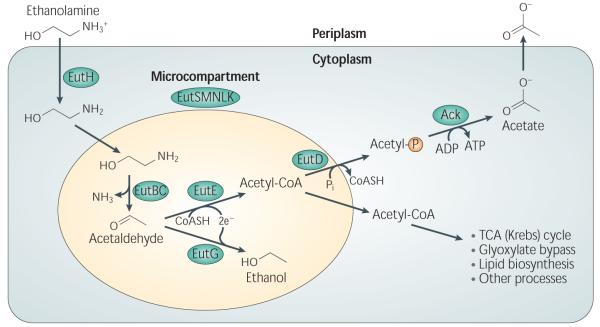
Figure 1.
Model for ethanolamine catabolism. Adapted from Brinsmade et al. 19. Ethanolamine enters the cell through diffusion or with the help of EutH. Within the ethanolamine-specific microcompartment, ethanolamine is degraded to acetaldehyde and ammonia by EutBC, which requires the co-factor AdoCbl. Acetaldehyde can be catabolized to alcohol by EutG or the metabolically useful compound, acetyl-CoA, by EutE. Acetyl-CoA can be used in a variety of metabolic processes or made into acetylphosphate by EutD. By substrate level phosphorylation, Ack can generate ATP and acetate from acetylphosphate.