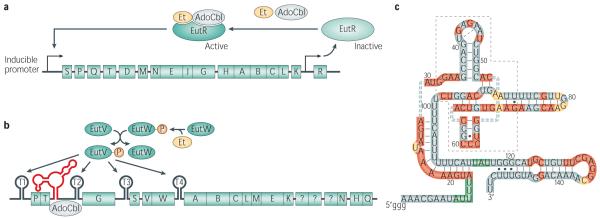
Figure 2.
Regulatory features of the eut operons in S. typhimurium (A) and E. faecalis (B). (A) The message encoding EutR is produced at a low-level from constitutive promotor P2. The inactive regulator is thought to sense the presence of ethanolamine and AdoCbl by direct binding which changes the conformation to the active form, promoting transcription of the entire eut operon from promoter P1. (B) Upon ethanolamine binding, the sensor kinase EutW autophosphorylates followed by phosphotransfer to the response regulator EutV. Activation of the two-component system by phosphorylation leads to disruption of terminators present in the message, likely by direct binding, allowing transcriptional read-through. The untranslated region proximal to the T2 terminator also contains a riboswitch, which upon binding to AdoCbl additionally promotes antitermination. P = promoter, T = terminator, blue boxes with letters represent the various eut genes mentioned in this review. The question marks represent genes whose identity is still controversial.