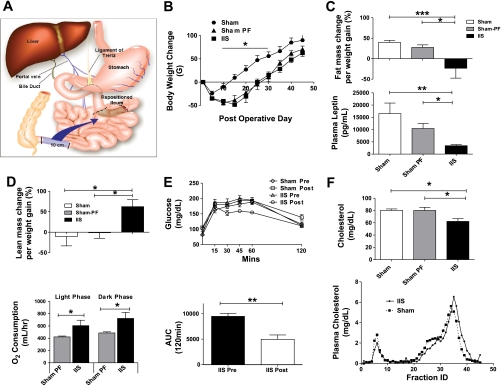
Fig. 1.
A: illustration depicting ileal interposition surgery. 10 cm of distal small intestine, starting 1 cm proximal to the ileo-cecal junction, is repositioned to the proximal jejunum. This is done by interpositioning the transected segment just beyond the ligament of Treitz. The segment is moved intact with all neurovascular connections and repositioned in a properistaltic direction. B: body weight change post surgery. Rats in the ileal interposition (IIS) surgery group lost more body weight compared with rats in the sham (SH) surgery group. There was a decrease in food intake in the IIS group. For groups IIS, SH, and SH-PF (sham surgery with pair-feeding to an IIS counterpart), n = 6, 7, 8, respectively (*P < 0.05). C: body fat mass change and plasma leptin levels. Magnetic resonance body composition analysis was performed on all rats prior to surgery and then subsequently a second time prior to death during the 5th wk after surgery. The weight gained by the SH and SH-PF groups had an increase in their proportion of fat tissue mass while IIS surgery group less fat mass as a percentage of new body weight gained compared with baseline. Plasma leptin levels were measured at completion of study. For groups IIS, SH, and SH-PF, n = 6, 7, or 8. (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001). D: body lean mass change and oxygen consumption. The weight gained by the SH and SH-PF groups had no change in their proportion of lean tissue mass, while the IIS surgery group had more lean mass as a percentage of new body weight gained compared with baseline. For groups IT, SH, and SH-PF, n = 6, 7, and 8, respectively. (*P < 0.05). Energy expenditure studies were conducted in the 5th wk after surgery. Oxygen consumption was higher in IIS rats compared with weight-matched SH-PF rats when observed in metabolic cages and given ad libitum access to a high-fat diet for 3 days (*P < 0.05; n = 7 per group). E: glucose tolerance after ileal interposition. Oral glucose tolerance tests were conducted prior to surgery (presurgery) and during the 5th wk after surgery (postsurgery). Rats in the IIS group had an improvement in their glucose tolerance with area under the curve (AUC) for 120 min being significantly less (**P < 0.01). F: plasma cholesterol levels and Fast-performance liquid chromatography (FPLC) fractions after ileal interposition. IIS rats lower plasma cholesterol levels compared with both SH and SH-PF controls. This was also a 25% reduction from presurgery circulating plasma cholesterol levels in the IIS group. For groups IIS, SH, and SH-PF, n = 7, 8, and 8, respectively. (*P < 0.05). Qualitative FPLC fraction analysis of plasma cholesterol lipoproteins heavier HDL particles were observed more in the IIS postsurgery rats (pooled plasma from n = 7 per group).