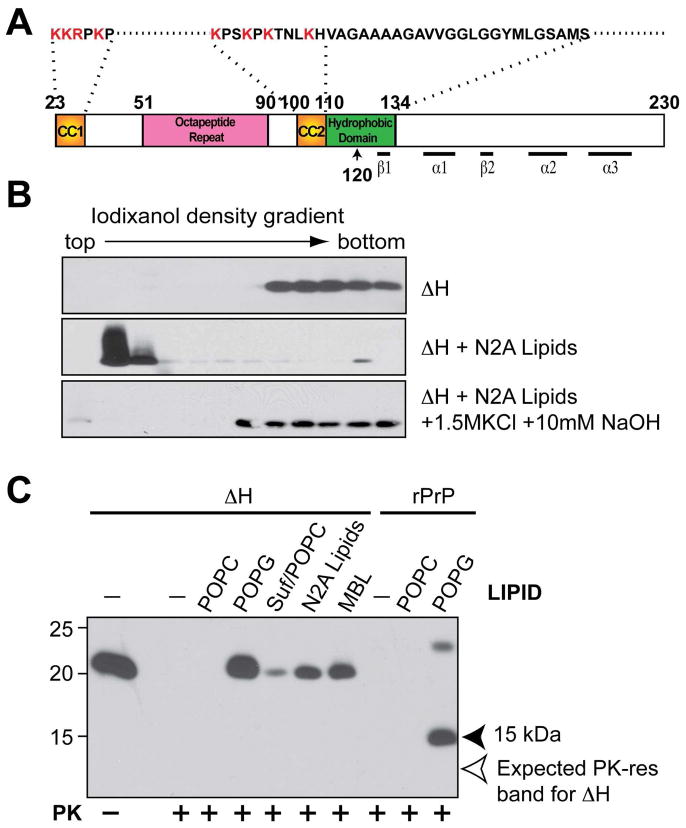
Figure 2. The highly conserved hydrophobic domain of PrP is required for hydrophobic rPrP-lipid interaction.
(A) Illustration of mouse PrP23-230. The amino acids were numbered according to mouse PrP sequence. (B) Iodixanol density gradient analyses of mouse rPrPΔH alone, rPrPΔH + total lipids isolated from N2A neuroblastoma cells (N2A lipids), rPrPΔH + N2A lipids extracted with the 1.5 M KCl plus 10 mM NaOH solution. (C) Mouse rPrP or rPrPΔH were incubated with indicated lipids for 1 hour and subjected to PK digestion. Solid arrowhead points at the 15 kDa PK-resistant band generated from wild-type rPrP. Empty arrow points at the expected position of PK-resistant band of rPrPΔH. Suf, Sulfatide; Suf/POPC, sulfatide and POPC at a mass ratio of 1:1; MBL, mouse brain lipids. PrP was detected by immunoblot analysis with POM1 antibody.