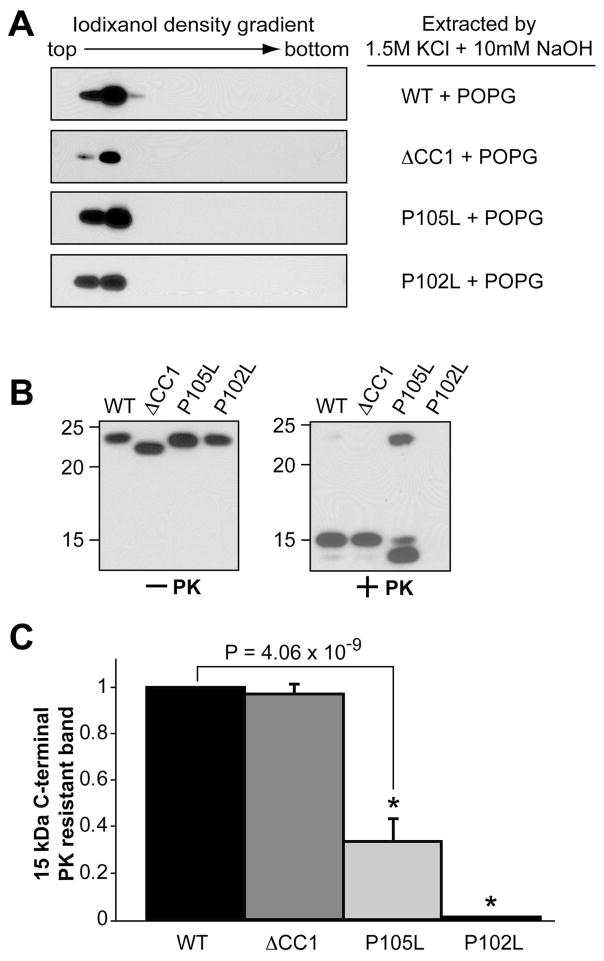
Figure 6. Disease-associated P105L and P102L mutations and N-terminal positively charged region affect lipid-induced rPrP conformational change in different manners.
(A) Wild type human rPrP, ΔCC1, P105L, or P102L mutant was incubated with POPG and then extracted by an alkaline solution of 1.5M KCl and 10mM NaOH prior to the iodixanol density gradient analysis. (B) Wild type human rPrP, ΔCC1, P105L, or P102L were incubated with POPG for 1 hour and subjected to PK digestion. PrP was detected by immunoblot analysis with POM1 antibody. (C) Densitometric analyses of PK digestion results in (B). The density of the 15 kDa PK-resistant band of wild-type rPrP was set as 1. The density of the 15 kDa band of ΔCC1, P105L or P102L mutant was used to calculate the PK resistance. The PK-digestion assay was repeated 3 times for each sample. The error bar represents the standard deviation and the asterisk indicates a significant difference.