Fig.1.
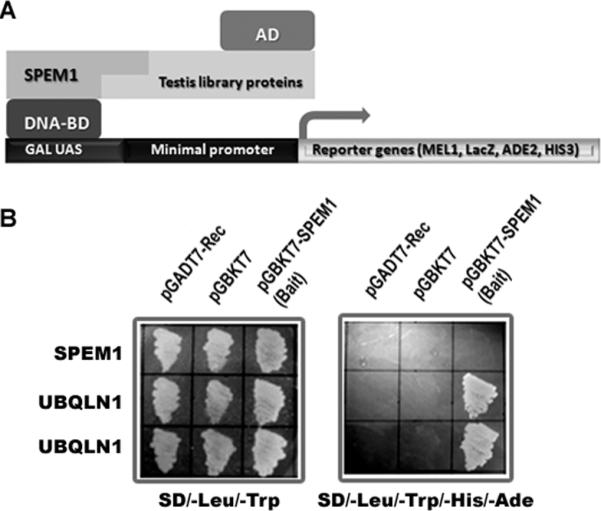
Identification of UBQLN1 as a SPEM1-interacting protein using yeast 2-hybrid (Y2H) assay. (A) In the Y2H assay, SPEM1 was used as bait and an adult mouse testis library was screened. Interactions between SPEM1 and any testicular proteins would activate the expression of reporter genes, leading to yeast cell growth on selective medium. (B) Yeast co-transformation assays to confirm interactions between SPEM1 and two independent clones expressing UBQLN1. On the non-selective plates (SD/-Leu/-Trp) all transformed yeast cells grew, indicating viability of the cells and non-toxicity of the plasmids. Only cells co-transformed with pGBKT7-SPEM1 and pGDT7-UBQLN1 grew on the selective plates (SD/-Leu/-Trp/-His/-Ade), demonstrating true interactions between UBQLN1 and SPEM1 in yeast cells.
