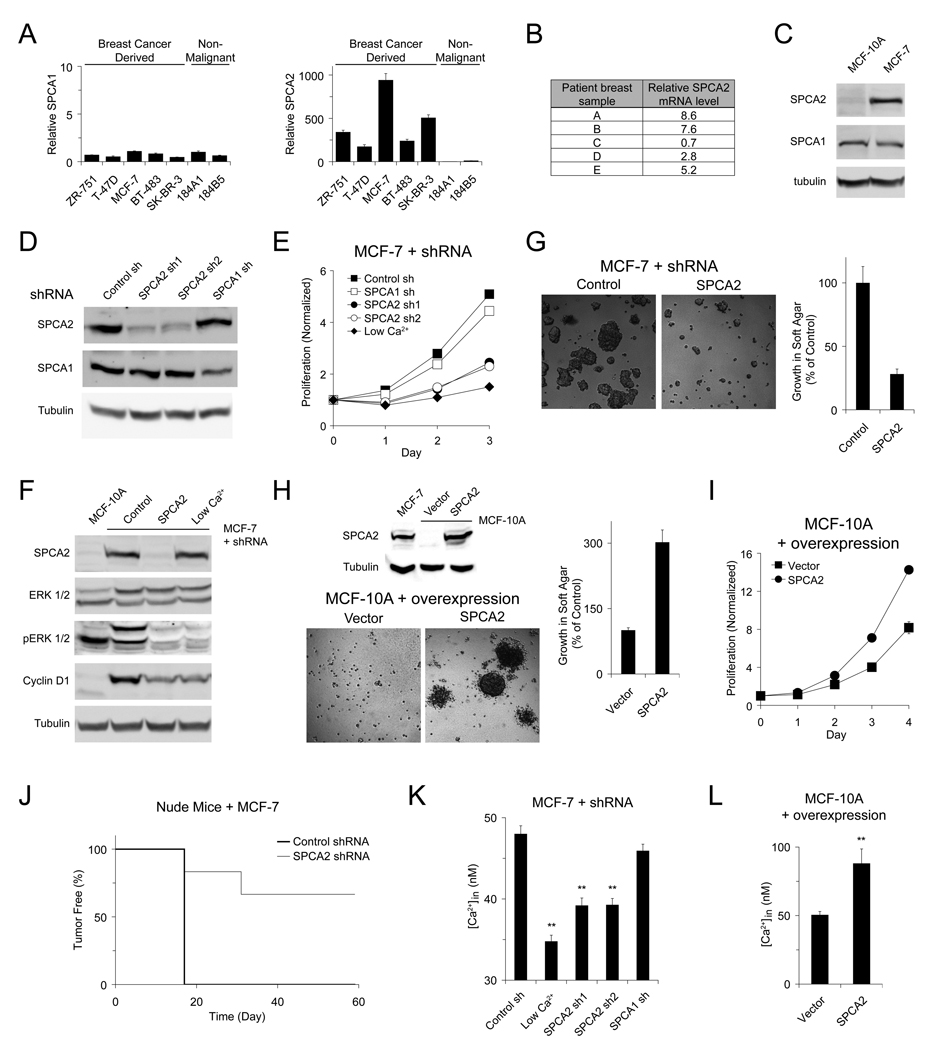
Figure 1. Upregulation of SPCA2 induces oncogenic signaling in mammary tumor cells.
mRNA levels were measured by quantitative real-time RT-PCRs and normalized to 18S rRNA in (A) a panel of breast epithelial cell lines relative to 184A1 and (B) in human breast tumor samples compared to matched normal surrounding breast tissue. n = 3 in (A). (C) Immunoblot of SPCA expression in MCF-10A and MCF-7 cells. Immunoblot (D) and normalized proliferation (E) of MCF-7 cells lentivirally transduced with shRNA against SPCA isoforms. n = 3 in (E). (F) Immunoblot of ERK 1/2 phosphorylation and Cyclin D1 expression in MCF-7 cells transduced with shSPCA2. Micrographs and normalized growth of (G) MCF-7 cells with SPCA2 knockdown or (H) MCF-10A cells with SPCA2 overexpression in soft agar. n = 3. Immunoblot showing relative SPCA2 expression levels in (H). (I) Normalized proliferation of MCF-10 cells with SPCA2 overexpression. n = 3. (J) Tumor incidence in nude mice injected with MCF-7 cells; n = 6, P = 0.005 (log-rank test). (K) Basal Ca2+ levels in MCF-7 cells with SPCA2 knockdown. From left to right: n = 80, 80, 77, 81, 69. ** P < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). (L) Basal Ca2+ levels in MCF-10A cells with SPCA2 overexpression. Vector, n = 23; SPCA2, n = 23. ** P < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). Error bars represent standard error (K and L) or standard deviation (A, E, G, H and I).