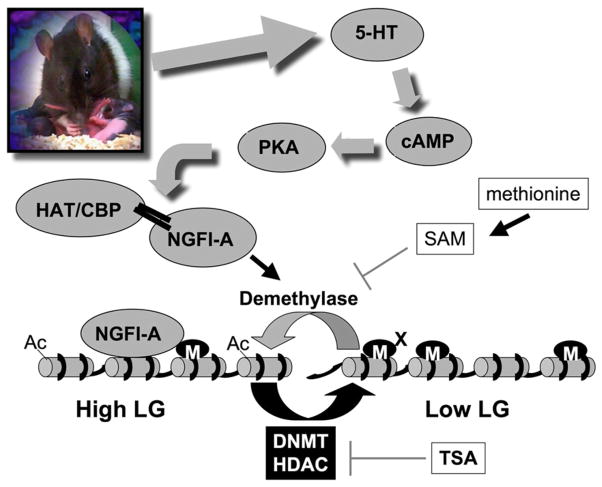
Fig. 2.
Epigenetic reprogramming by maternal care; a model. Maternal licking and grooming (LG) in the rat triggers activation of 5-HT receptors in the hippocampus leading to increased intracellular cAMP, activation of the transcription factor NGFI-A and recruitment of the HAT CBP to the GR exon 17 promoter. Acetylation of histone tails facilitates demethylation. In offspring of Low LG mothers, this process is reduced in comparison with offspring of High LG mothers, leading to differential epigenetic programming of the GR promoter. In the adult rat, the epigenetic state is reversible. TSA, an HDAC inhibitor, increases histone acetylation and facilitates demethylation and epigenetic activation of the gene in the offspring of the Low LG mothers. Conversely, injection of methionine to adult offspring of the High LG mothers leads to increased SAM, inhibition of demethylation, increased DNA methylation, and reduced activity of the GR exon 17 promoter.