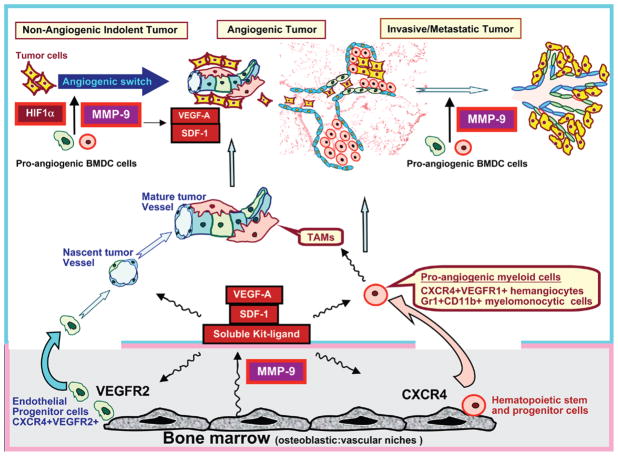
Figure 1. Multifaceted Role of MMP-9 in Supporting Mobilization and Recruitment of Bone Marrow-Derived Cells in Tumor Vasculogenesis and Neoangiogenesis.
Activated MMP-9, through increasing the bioavailability of Kit-ligand, VEGF-A, and SDF-1, supports the mobilization of the proangiogenic bone marrow-derived cells (BMDCs), including tumor-associated monocytes/macrophages (TAMs), Gr1+CD11b+ myeloid precursors, CXCR4+VEGFR1+ hemangiocytes, and EPCs to the circulation. Irradiation-induced vascular injury or hypoxia-driven upregulation of HIF-1α enhances the release of SDF-1 and VEGF-A, thereby recruiting MMP-9-bearing BMDCs to the neoangiogenic niches, augmenting tumor vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, invasive potential, and metastasis. MMP-9 delivered by BMDCs amplifies tumor neoangiogenesis by increasing the bioavailability of VEGF-A and stem cell active chemocytokines, including SDF-1 and Kit-ligand.