Figure 5.
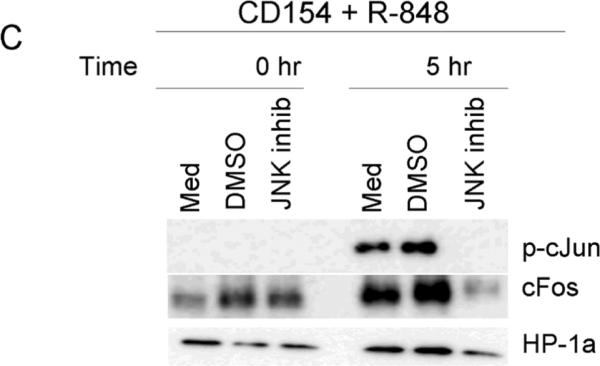
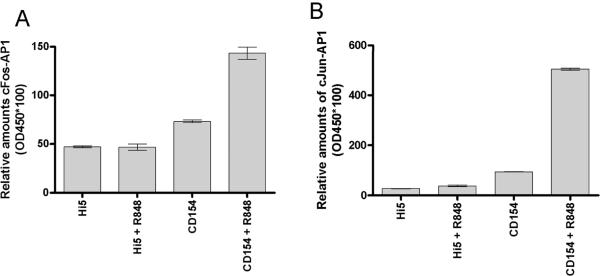
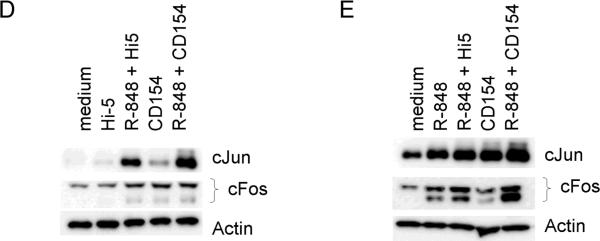
Differential activation of AP-1 monomers following dual signaling. Mouse cells were stimulated and nuclear extracts subjected to an EMSA based ELISA. Background normalized (described in materials and methods) absorbance values at 405nm are given for cJun (A) and cFos (B). There were no differences between treatments for other AP-1 monomers tested (Fra1, Fra2, JunB, JunD, and FosB, data not shown). Data are representative of two individual experiments. C) Nuclear extracts of B cells stimulated with both CD154 and R-848 in the presence or absence of JNK inhibitor. Inhibitor was added to cell cultures 30 minutes prior to stimulation. HP-1a (heterochromatin-associated protein 1a) was used as a nuclear extract loading control. D) Mouse B cells and E) human B cells were stimulated with R-848 with or without CD154 or controls. Dual stimulation increased the level of total cJun and cFos in both mouse and human B cells. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments.