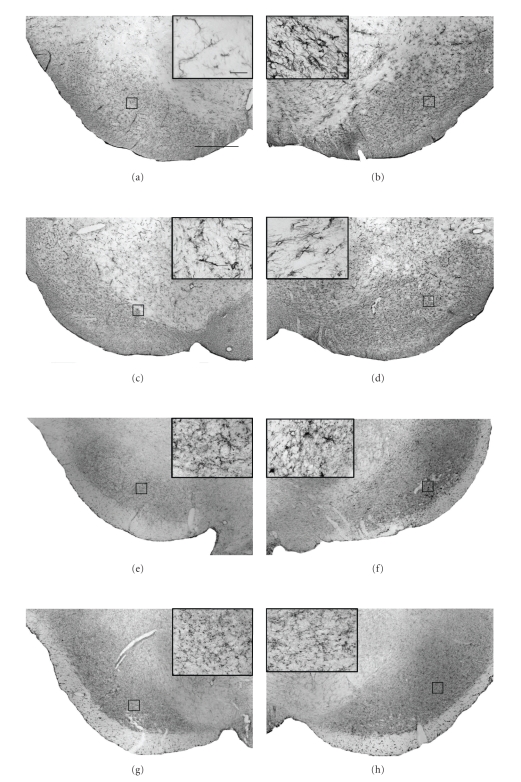
Figure 3.
Neuroprotection against 6-OHDA toxicity following delayed subchronic intranigral administration of 2R,4R-APDC is associated with qualitative reductions in inflammatory markers. Representative photomicrographs (×40) of DAB/peroxidase staining for GFAP (astrocytosis) and OX-42 (microgliosis) in the SNc from each treatment group (scale bar 200 μm.). Panels (a)–(g) show the intensity and distribution of GFAP+ and OX-42+ cells in the contralateral control SN of vehicle (a), (c) and (e), (g) 2R,4R-APDC (10 nmol)-injected animals. Panels (b)–(h) show the intensity and distribution of GFAP+ and OX-42+ cells in the Lesioned SNc of vehicle (b), (d) and (e), (g) 2R,4R-APDC (10 nmol)-injected animals. (Insets (a)–(h)), ×60, enlargements of outlined areas (scale bar 10 μm)). Note the apparent reduction in intensity of GFAP+ and OX-42+ staining in 2R,4R-APDC-injected animals compared to vehicle-treated animals. Further, 2R,4R-APDC treatment appeared to reduce the number of cells with morphology characteristic for reactive astrocytes or activated microglia in the SNc in comparison to vehicle-treated controls.