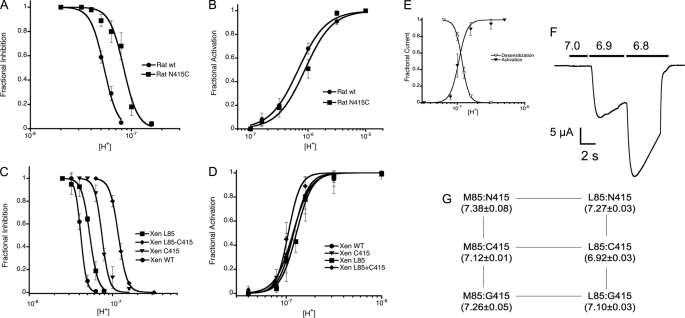
FIGURE 4.
The substitution N415C decreases the apparent proton affinity of ASIC1. A, dose-response relationships of rat ASIC1a wild type and mutant N415C to desensitization by external protons. The activating pH was 6.8. B, the dose response of rat ASIC1a to activation by protons. The preconditioning pH was 7.4 for all measurements. C, the dose response of desensitization by protons of Xenopus (Xen) ASIC1.1 wild type and the indicated mutants. The activating pH was 7.0. D, dose response of activation of xASIC1.1 by protons preconditioning by pH 7.6. E, overlap of activation and desensitization curves of the double mutant xASIC1.1-M85L/N415C. For all graphs, data points are the mean ± S.D. of at least six independent measurements. Lines are the fit of the data to Equation 1. F, currents evoked by sequential increases in the concentration of protons without returning the pH to 7.8 between stimuli. G, pH50D changes of multiple amino acid substitutions in the pair of residues 85 and 415 of xASIC1.1. pH50D values, mean ± S.D. are shown in parentheses below each mutant.