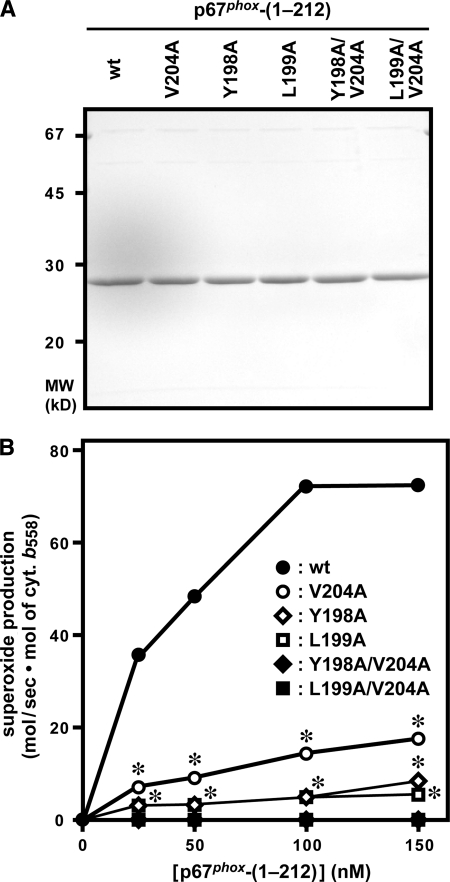
FIGURE 3.
Role for Tyr-198, Leu-199, and Val-204 of p67phox in activation of the phagocyte NADPH oxidase under cell-free conditions. A, SDS-PAGE analysis of purified p67phox proteins that were used in a cell-free system for activation of the phagocyte NADPH oxidase. Wild-type (wt) p67phox-(1–212) or a mutant protein carrying the V204A, Y198A, L199A, Y198A/V204A, or L199A/V204A substitution was subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by staining with Coomassie Brilliant Blue. The positions for marker proteins are indicated in kilodaltons. B, role for Tyr-198, Leu-199, and Val-204 of p67phox in a cell-free system for activation of the phagocyte NADPH oxidase. Human neutrophil membrane (10 μg/ml) as a source of the gp91phox-p22phox dimer was mixed with a mutant or wild-type p67phox protein at the indicated concentrations, 100 nm Rac1 (Q61L), and 100 nm GST-p47phox-(1–286). The mixture was incubated for 2 min at 25 °C with 100 μm SDS, and the reaction was initiated by the addition of 200 μm NADPH. The NADPH-dependent superoxide-producing activity was measured by the rate of superoxide dismutase-inhibitable cytochrome c reduction, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Compared with the whole cell system, much higher amounts of superoxide were produced in the cell-free system, which enabled us to use the cytochrome c reduction method. Each graph represents the means ± S.D. of data from three independent experiments. *, p < 0.01 versus the mutant p67phox with the Y198A/V204A or L199A/V204A substitution.