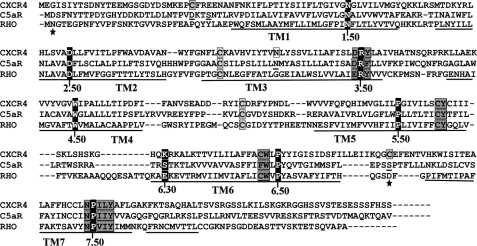
FIGURE 1.
Sequence alignment of CXCR4 and C5aR with rhodopsin highlighting the most conserved residues and the known activation switches in GPCRs. Ballesteros and Weinstein nomenclature assigns X.50, to the “fingerprint residues” shown as white letters with black background in each transmembrane domain. Important transmembrane activation domains are shaded in gray. Conserved cysteine residues participating in disulfide bond formation are shown with gray boxes. Residues shown with black boxes indicate lack of complementary charged residues at 6.30 to support the ionic lock activation switch. Point mutation known to confer constitutive activity in CXCR4 is shown with white box. Residues shown as underlined have been subjected to mutagenesis for engineering C5aR. Residues marked with stars have been mutated to cysteine in other studies for engineering an extra disulfide bond between EC3 and N terminus of rhodopsin.