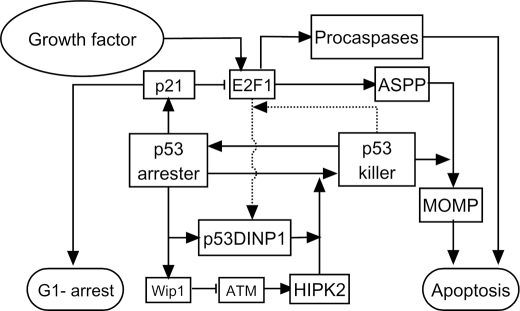
FIGURE 3.
Cell fate decision module model. Active p53 is divided into p53 arrester and p53 killer. p53 arrester is a primarily phosphorylated form of p53 on Ser-15 and Ser-20, whereas p53 killer is a further phosphorylated form of p53 on Ser-46. p53 arrester induces cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase by inducing p21, which inhibits E2F1 activity, whereas p53 killer induces expression of proapoptotic genes. The conversion between p53 arrester and p53 killer is controlled by Wip1 and p53DINP1. E2F1 can be activated by growth factors. p53 killer and E2F1 cooperate to transactivate p53DINP1. With the help of E2F1-induced ASPP, p53 killer induces expression of p53AIP1 and Bax, which results in mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP). Moreover, E2F1 promotes apoptosis by up-regulating several key proapoptotic factors including Apaf-1 and procaspase-9 and -3.