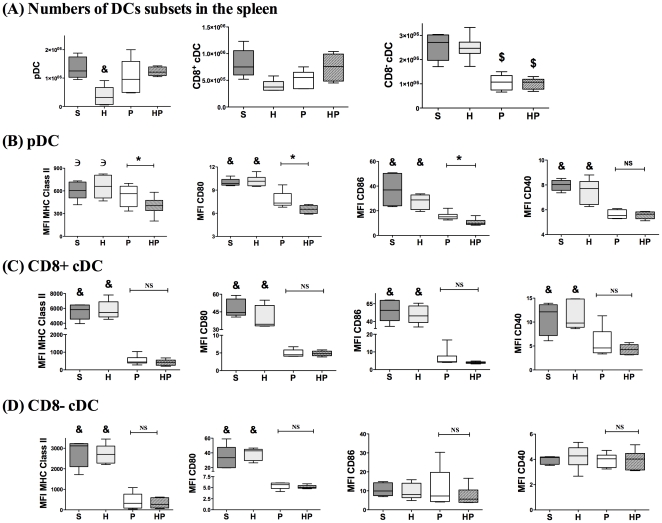
Figure 7. Hemorrhagic shock prior to methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA) pneumonia induced phenotypic alterations of plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs).
Four groups of mice were studied: sham-treated (S group), hemorrhaged mice (H group), MSSA-induced pneumonia only (P group), and hemorrhage before MSSA-induced pneumonia (HP group). Spleens were harvested 24 hours after sepsis onset. (A) Cells obtained from spleen homogenates were counted. The percentage of each subset of DCs was determined by a FACS analysis and number of each DCs subset was calculated. DCs subsets were defined by specific membrane markers: B220 and siglec H for pDCs, CD11c and CD8 to differentiate CD8+ conventional DCs (cDCs) and CD8− cDCs. Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of MHC class II, CD80, CD86, and CD40 molecules on (B) pDCs, (C) CD8+ cDCs, and (D) CD8− cDCs was assessed. Data are representative of two independent experiments (each group, n = 6). Boxes represent median (interquartile range). & P<0.05 versus P and HP groups, € P<0.05 versus HP group, *P<0.05.