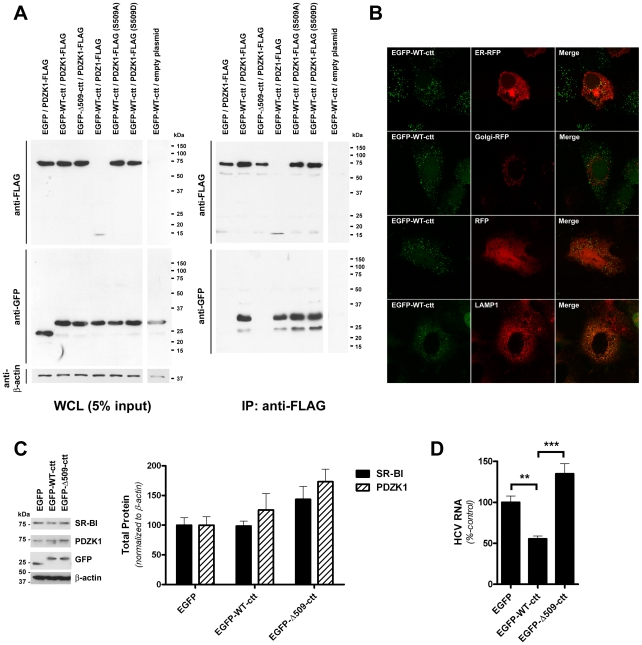
Figure 6. A green fluorescent protein chimera of the SR-BI C-terminus interacts with PDZK1 and inhibits HCVcc infection.
(A) 293T cells were co-transfected with expression vectors encoding the indicated chimeric GFP-SR-BI cytoplasmic C-terminus (cct) (aa 479-509 or 479-508) expression construct and PDZK1 expression construct prior to immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody and Western analysis of immunoprecipitates using anti-FLAG or anti-GFP antibodies as indicated (right panels). Expression of each of the FLAG- and GFP-tagged proteins, relative to the loading control β-actin, in whole cell lysates (WCL) prior to IP is shown in the left panel. (B) Laser-scanning confocal microscopy analysis of the localization of EGFP-WT-ctt. Huh-7 cells stably expressing EGFP-WT-ctt were grown on gelatin-coated coverslips, transfected with the indicated red fluorescent protein (RFP) expression construct (where applicable) and processed for direct detection of fluorescent protein-associated epifluorescence or indirect immunofluorescent detection of LAMP1. Merged images are shown in the right panels. (C) Western analysis of SR-BI (∼85 kDa), PDZK1 (∼70 kDa), EGFP (∼25 kDa), EGFP-WT-ctt (∼32 kDa) and EGFP-Δ509-ctt (∼32 kDa) protein levels in Huh-7 cells stably expressing the indicated EGFP construct. β-actin (∼42 kDa) was used as a loading control. SR-BI and PDZK1 protein levels were quantified by densitometry and normalized to those of β-actin (graph inset). Data are means + SEM (n = 3). (D) Huh-7 cells stably expressing the indicated EGFP chimera were incubated with HCVcc (Jc1/Myc; approximate multiplicity of infection: 0.3) for 3 h, washed and returned to culture for 72 h prior to quantification of HCV RNA levels (normalized to RPLPO mRNA). HCV RNA levels are expressed relative to those of EGFP-expressing control cells. Data are means + SEM (n = 4). **, P<0.005; ***, P<0.001.