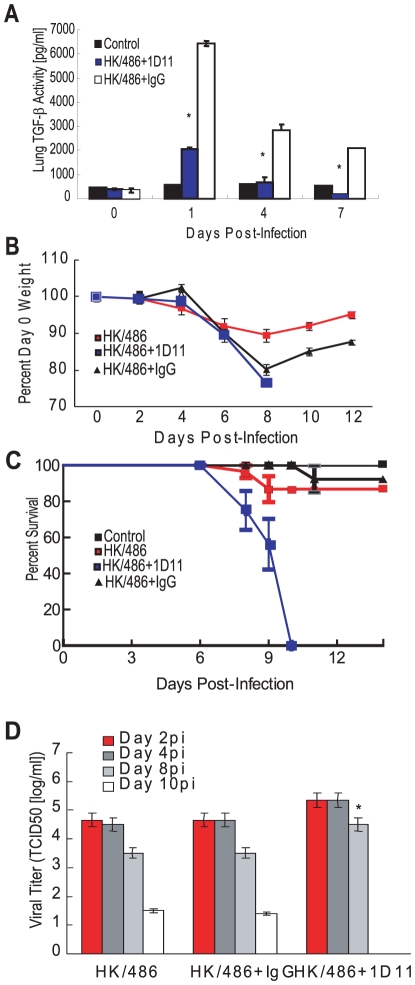
Figure 7. Depletion of TGF-β alters morbidity in HK/486-infected mice.
Six hours before infection, BALB/c mice were treated with a TGF-β neutralizing antibody (1D11) or an isotype control antibody (IgG) at a dose of 0.5 mg/mouse and subsequently inoculated with PBS (control) or 105 TCID50 units of HK/486 virus (n = 15). Antibodies were readministered every 48 hpi. At 0, 1, 4, and 7 days pi, total TGF-β levels were analyzed in lung homogenates by a mouse TGF-β-specific ELISA (A). Weights (B) and survival (C) were monitored for 14 dpi. On days 2, 4, 8, and 10 pi, lung homogenates were monitored viral titers by TCID50 analysis on MDCK cells (D). Error bars represent standard error of the mean. Asterisk (*) indicates significant decrease in TGF-β levels as compared with infected group treated with IgG (A), and increase in viral titers as compared with HK/486-infected mice with and without IgG treatment (D).