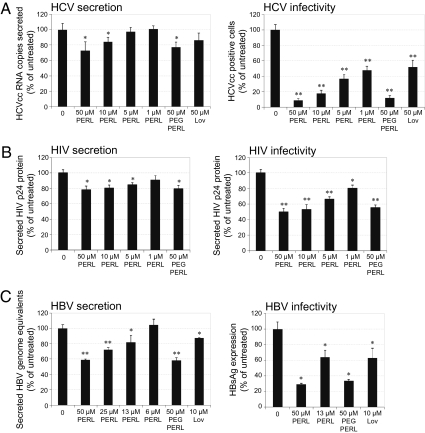
Fig. 2.
PERL treatment significantly decreases the secretion and infectivity of HCV, HBV, and HIV virus particles. (A) Huh7.5 cells were infected with Jc1 HCVcc at a MOI of 0.5 and were treated for 4 d. Secretion of HCVcc particles after the treatment period was quantified by real-time PCR of RNA within cell-culture supernatant, and infectivity of secreted particles was determined by reinfecting naïve Huh7.5 cells with cell supernatant normalized to RNA levels and measuring the level of infection 2 d later by HCV core protein immunofluorescence. (B) PBMCs were infected with HIV-1 primary isolate, LAI, at TCID50 = 100. Infected cells were treated for 4 d, at which time secreted HIV particles were quantified in the cell-culture supernatant by capture p24 ELISA. Infectivity was determined following reinfection of naïve PBMCs with normalized cell supernatant and measuring HIV secretion after a 3-d incubation period by capture p24 ELISA. (C) HepG2.2.2.15 cells stably transfected with two copies of the HBV genome were treated for 4 d; then HBV viral particles were purified and quantified by real-time PCR. Infectivity assays were performed by normalizing virus particles and infecting differentiated HepaRG cells. Infected HepaRG cells were harvested 9 d postinfection, and intracellular viral antigens were quantified to determine the level of infection. Data represent the mean and SD of three independent experiments performed in triplicate and are presented as a percentage of the untreated samples. Significant differences from this value are denoted by *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.001 (t test).