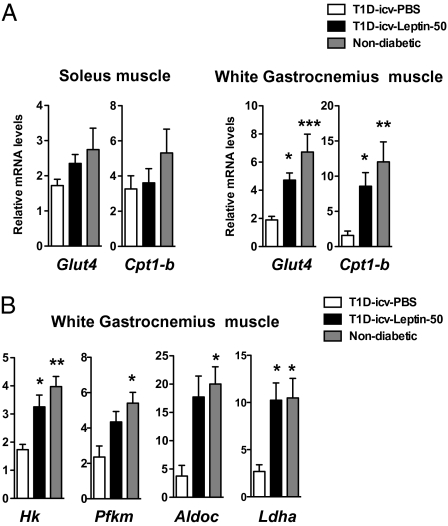
Fig. 5.
CNS leptin administration improves parameters related to glucose and fat metabolism in skeletal muscle. Glut4 and Cpt1-b mRNA levels in soleus muscle and white gastrocnemius muscle (A) and mRNA levels of glycolytic pathway enzymes in WG muscle (B) in T1D-icv-PBS and T1D-icv-Leptin-50 mice 10 d following stereotaxic surgery and in age-matched nondiabetic control mice. Error bars represent SEM (n = 4–7). Statistical analyses were done using one-way ANOVA (Tukey's posttest). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 vs. T1D-icv-PBS mice.