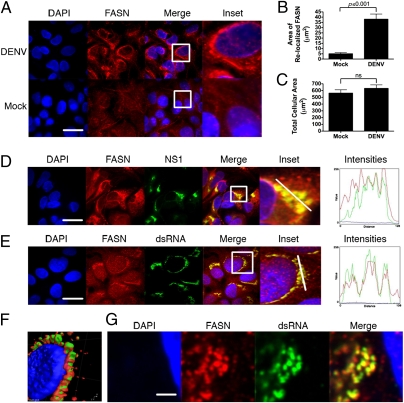
Fig. 2.
FASN is relocalized to sites of DENV replication. (A) Huh-7.5 cells were mock- or DENV-infected at a multiplicity of infection of 1–5, fixed 36–48 h postinfection, and probed with a monoclonal antibody against FASN. Insets reflect zoomed areas of the boxed regions. (Scale bar: 30 μm.) ImageJ quantitation of the fluorescent intensity of FASN staining in DENV-infected cells (B) compared with mock-infected cell size and cell size in DENV-infected or mock-infected cells (C) (average ± SEM). ns, not significant. Infected cells were probed with antibodies against FASN and the DENV NS1 (D) or dsRNA (E), the DENV replication intermediate. Insets reflect zoomed areas of the boxed regions. (Scale bar: 30 μm.) (F) 3D reconstruction of a z-stack taken through a DENV-infected cell stained with antibodies to dsRNA (green) and FASN (red). (G) Two-photon microscopy of a DENV-infected cell probed for dsRNA and FASN. Intensities plots represent the fluorescent intensity of red, green, and blue pixels along the white line in the inset panels. (Scale bar: 1,500 nm.)