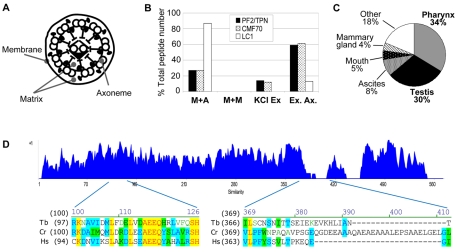
Fig. 1.
CMF70 is a conserved component of motile flagella. (A) Cross-section cartoon of a flagellum showing compartments separated by biochemical fractionation. (B) Relative number of peptides identified by Pazour and colleagues (Pazour et al., 2005) in mass spectrometry analyses of C. reinhardtii flagellar fractions corresponding to tergitol-insoluble membrane plus axoneme (M+A), Nonidet-soluble membrane plus matrix (M+M), Nonidet-insoluble axonemes extracted with 0.6 M KCl to yield solubilized extract (KCl Ex) and insoluble extracted axonemes (Ex. Ax.). Data from Pazour and colleagues (Pazour et al., 2005) are tabulated for PF2/trypanin, CMF70 and LC1. The distribution of peptides is similar for PF2/trypanin and CMF70, but different for the outer dynein subunit LC1. (C) Expression profile of the human CMF70 homologue shows enrichment in ciliated tissues (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/UniGene/). (D) Amino acid sequence similarity plot (Vector NTI, Invitrogen) of CMF70 homologues from T. brucei (Tb), C. reinhardtii (Cr) and H. sapiens (Hs). A value of +1 is corresponds to a stretch of identical amino acids. Representative regions of high similarity (residues 97–124) and low similarity (residues 366–408) are shown below the chart. Strictly conserved positions are highlighted in yellow, whereas residues identical in two of three sequences are highlighted in blue and conservative substitutions are green.