Fig. 2.
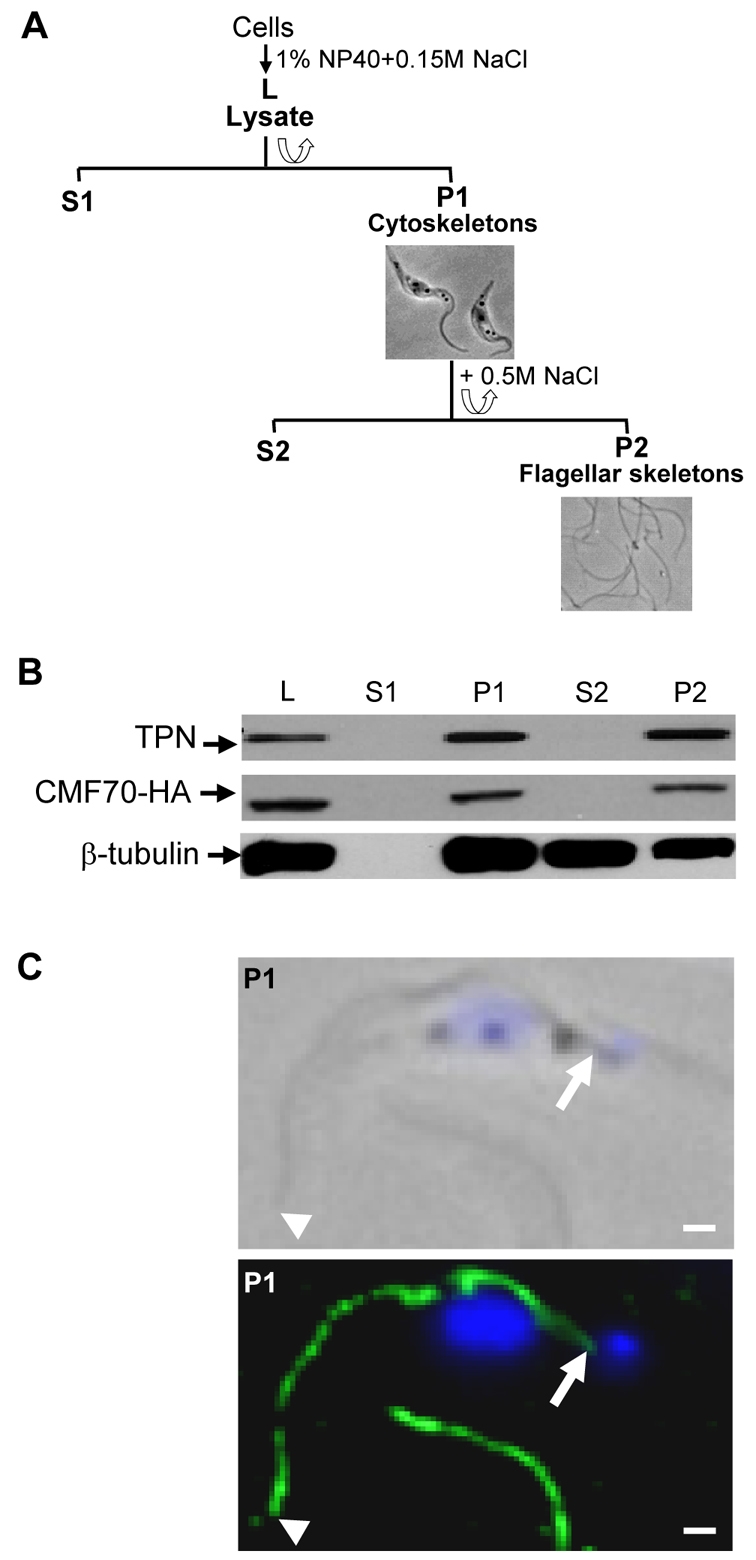
CMF70 is tightly associated with the T. brucei flagellar skeleton. (A) Flow chart depicting fractionation procedure to isolate T. brucei salt-extracted flagellar skeletons. Lysates (L) were prepared by extraction with 1% NP-40 and centrifuged for separation of detergent-soluble proteins (S1) from cytoskeletons (P1). The P1 fraction was further extracted with 0.5 M NaCl treatment to solubilize the subpellicular cytoskeleton (S2) and leave the flagellar skeletons (P2) intact. Corresponding phase-contrast images of cell (P1) and flagellar (P2) skeletons are shown. (B) Western blot analysis of whole-cell lysates and subcellular fractions prepared from HA-tagged CMF70 T. brucei cells shows a stable association of CMF70 and trypanin with the flagellar skeleton fraction (P2). The protein preparations were blotted with anti-HA (top panel), anti-trypanin (middle panel) and anti-β-tubulin (bottom panel) monoclonal antibodies. (C) Indirect immunofluorescence analysis. Cytoskeletons (P1) from CMF70-HA T. brucei cells were visualized after labeling with monoclonal anti-HA antibody (green) and DAPI (blue). Phase-contrast (top panel) and merged fluorescence (lower panel) images are shown. Arrowheads indicate the distal tip and arrows show the proximal end of the flagellum, near the kinetoplast. The flagellum of a second cell is visible at the bottom of the image. Scale bars: 1 μm.
