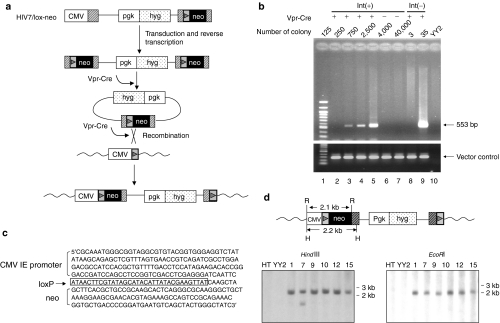
Figure 3.
Site-specific gene insertion with a Vpr-Cre containing lentiviral vector. (a) Steps involved in site-specific gene insertion with the targeting vector, HIV7/lox-neo. The vector backbone of HIV7/lox-neo contains the hyg gene controlled by the pgk promoter. The loxP-neo cassette was inserted into the 3′ LTR. Upon transduction and reverse transcription in transduced YY2 cells, this cassette would appear in both LTRs, thereby providing a substrate for recombination mediated by virion-associated Vpr-Cre. The resulting circular product containing a single loxP site can recombine with the target loxP site in the YY2 genome and insert the neo gene downstream from the CMV IE promoter. The insertion reaction presumably is catalyzed again by virion-associated Vpr-Cre. Wavy lines indicate the YY2 genomic DNA. (b) PCR detection of site-specific gene insertion events. YY2 cells were transduced with increasing amounts of HIV7/lox-neo with or without Vpr-Cre and selected in G418-containing medium. Upon selection for 2 weeks, various numbers of G418-resistant colonies as indicated were pooled and the genomic DNA was subjected to PCR amplification using a pair of primer specific for the CMV IE promoter and the neo gene. This pair of primer was expected to amplify a 533-bp fragment if gene targeting occurred (top). As a control, a second pair of primers that specifically amplified a 5′ HIV gag region present in the vector was also used in the PCR to demonstrate vector integration irrespective of the presence or absence of Vpr-Cre (bottom). Int(+), vectors containing a functional integrase; Int(−), vectors containing a defective integrase. The G418-resistance titers for the Int(+) and Int(−) vector were 25,000 ± 5,000 infectious units (IU)/ml and 38 ± 7 IU/ml, respectively. (c) The DNA sequence surrounding the neo gene insertion site. The 533-bp PCR fragment was cloned into pBluescript by TA cloning and sequenced. The loxP site was boxed. (d) Southern blot analysis of YY2-derived clones containing site-specific gene insertion. G418-resistant clones derived from the integrase-deficient HIV7/lox-neo vector were picked and expanded. The genomic DNAs from six such clones were digested with either HindIII or EcoRI, separated on a gel, blotted and hybridized with a neo-specific probe. The expected fragment size for site-specific gene insertion is 2.2 kb with HindIII digestion and 2.1 kb with EcoRI digestion. HT1080 DNA and YY2 DNA digested with HindIII or EcoRI were also run on the same gel to serve as negative controls. CMV, cytomegalovirus; GFP, green fluorescence protein; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; IE, immediate early; LTR, long-terminal repeat; Vpr, viral protein R.