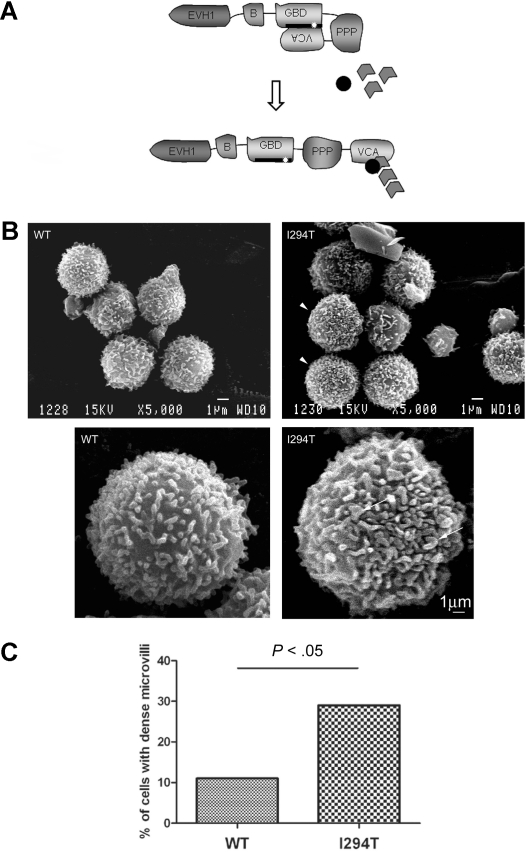
Figure 1.
WASpI294T lymphocytes demonstrate dysmorphic microvilli. (A) Schematic showing the modular domain structure of WASp. Before activation, WASp adopts an autoinhibited conformation in which intramolecular interaction of the VCA and GBD domains prevents binding of the Arp2/3 complex and monomeric actin to the carboxy terminus. The I294T mutation (white star) lies in the critical VCA binding region (thick black line; amino acids 242-310) and is predicted to disrupt VCA interaction, resulting in constitutive activation. (B) SEM micrographs of lymphocytes from a healthy donor (WT) and a patient with WASpI294T. WASpI294T cells show dense and frequently dysmorphic microvilli (arrowheads and arrows). Scale bars represent 1 μm. Images were acquired using a JEOL 6100 SEM operating at 15 kV and captured using Semafore software and processed (crop and brightness/contrast functions only) with Adobe Photoshop. (C) Lymphocytes were scored blindly for dense microvilli by 2 independent observers. At least 50 cells were scored for each of WASpWT and WASpI294T cells. A significantly greater percentage of WASpI294T cells assembled dense microvilli (P < .05 Fisher exact 1-tailed test).