Figure 1. Skeletal effects of Inhibins, Activin, BMPs and Follistatin derived from bone and gonadal sources.
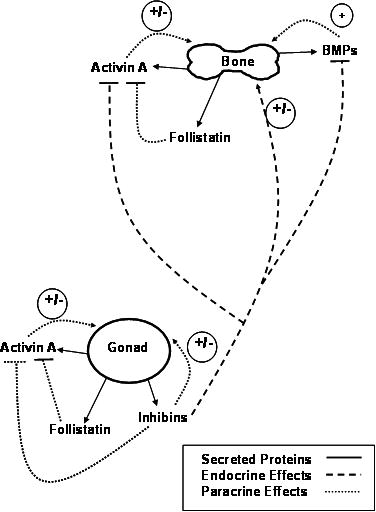
Skeletal effects of Activin A, its antagonist, Follistatin, and BMPs are paracrine effects (…….) from local production and sequestration of peptides in bone matrix. The stimulatory effects of Activin and BMP are blocked by the endocrine effects of Inhibins (- - - -) produced primarily by the gonads. The Inhibin antagonism of Activin and BMP action, demonstrating the importance of skeletal Inhibin “tone” that is associated with normal gonadal function. Activin A and Follistatin are also produced by the gonads, although their levels in serum are likely insufficient to exert endocrine effects on pituitary FSH production or contribute to the regulation of bone metabolism. See text for more details.
