Figure 5. Nucleotide-dependence of ribosomal association of ABCE1.
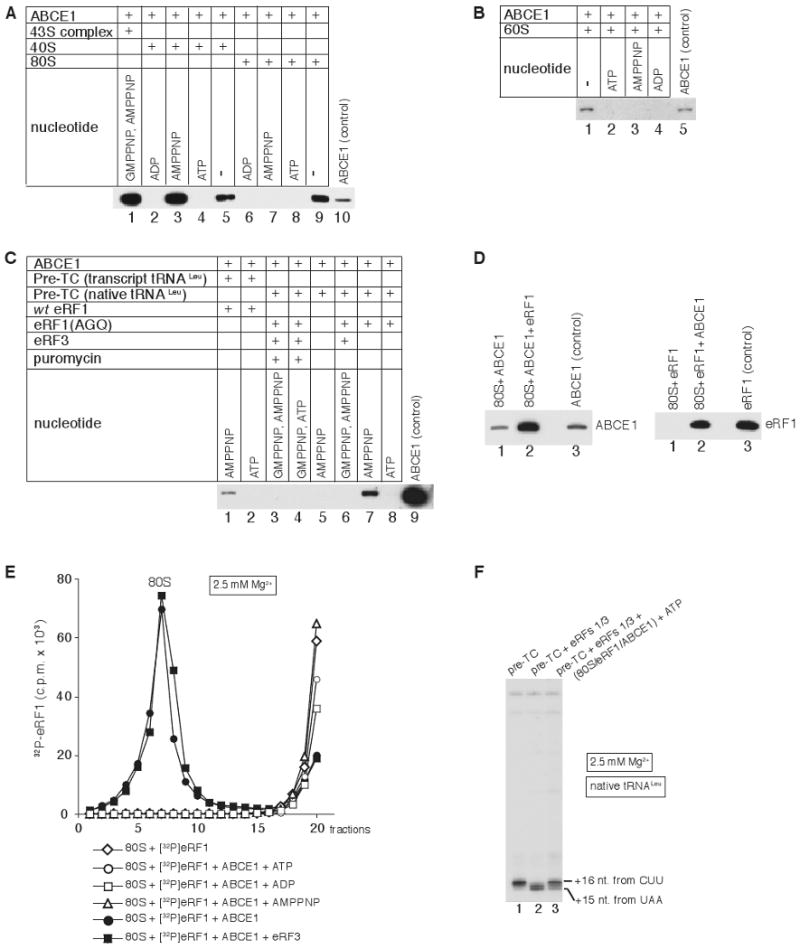
(A-C) Association of ABCE1 with (A) 40S subunits, 43S complexes and 80S ribosomes, (B) 60S subunits and (C) pre-TCs assembled with native or transcript Leu-tRNALeu and incubated with combinations of wt eRF1, eRF1(AGQ), eRF3 and puromycin, in the presence/absence of nucleotides, as indicated. Ribosomal peak fractions obtained by SDG centrifugation were analyzed by western blotting using anti-ABCE1 antibodies. (D) Association of ABCE1 and eRF1 with individual 80S ribosomes in the absence of nucleotides assayed by SDG centrifugation and western blotting of peak ribosomal fractions using anti-ABCE1 (left panel) and anti-eRF1 (right panel) antibodies. (E) Association of [32P]eRF1 with 80S ribosomes in the presence/absence of ABCE1 and nucleotides as indicated, assayed by SDG centrifugation. Upper fractions were omitted for clarity. (F) Toe-print analysis of ribosomal complexes obtained by incubating pre-TCs, assembled on MVHL-STOP mRNA using native tRNALeu, with eRF1/eRF3 and SDG-purified 80S/eRF1/ABCE1 complexes (panel E). Toe-prints corresponding to ribosomal complexes are indicated.
