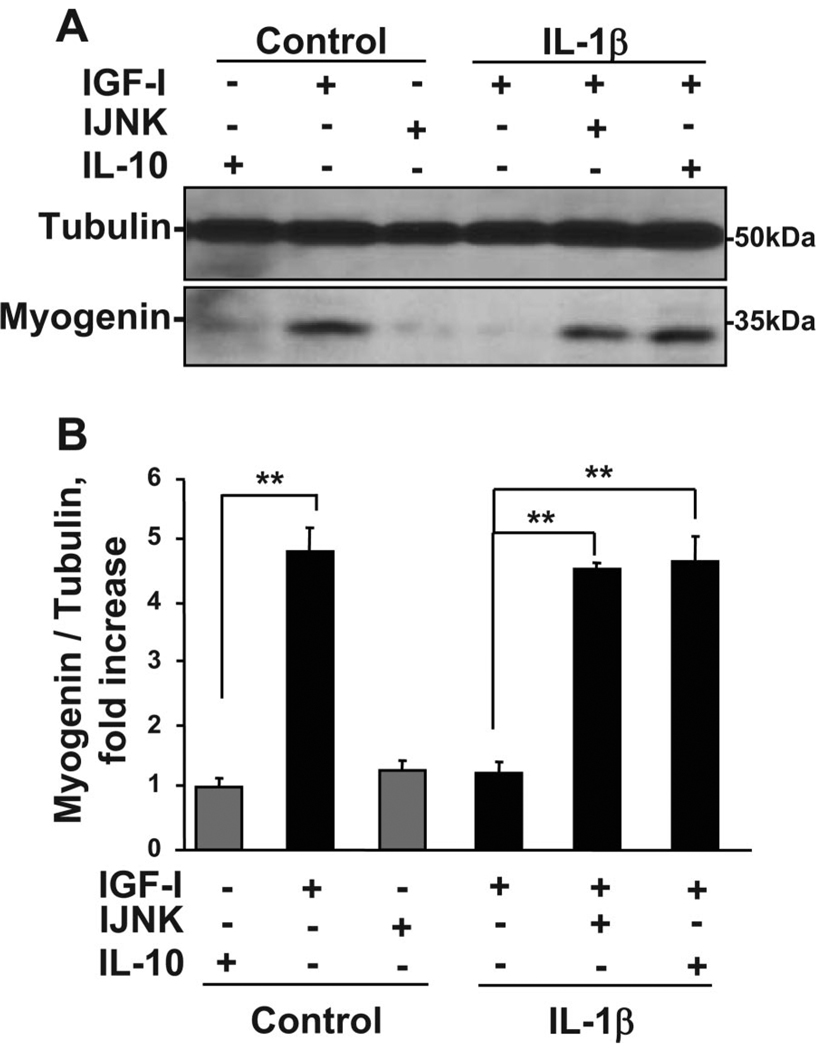
Fig. 6.
Both IL-10 and I-JNK suppress the ability of IL-1β to inhibit myogenin expression. C2C12 myoblasts were pretreated with an inhibitor of JNK, I-JNK (2 µM), or IL-10 (10 ng/ml) for 1 h before treatment with IL-1β (1 ng/ml) for another 1 h. Cells were than treated with IGF-I (50 ng/ml) for an additional 24 h to induce myogenin expression, which was determined by Western blotting with a monoclonal myogenin-specific antibody. Representative Western blots (A) and a densitometric summary (B) of 4 independent experiments demonstrated that IL-10 and I-JNK completely restored myogenin expression by suppressing IL-1β-induced inhibition of IGF-I biological activity. Neither IL-10 nor I-JNK altered myogenin expression in the absence of IL-1β. These results indicate that the protective biological activity of IL-10 in skeletal muscle development is expressed by inhibition of JNK. **P < 0.01.