Figure 7.
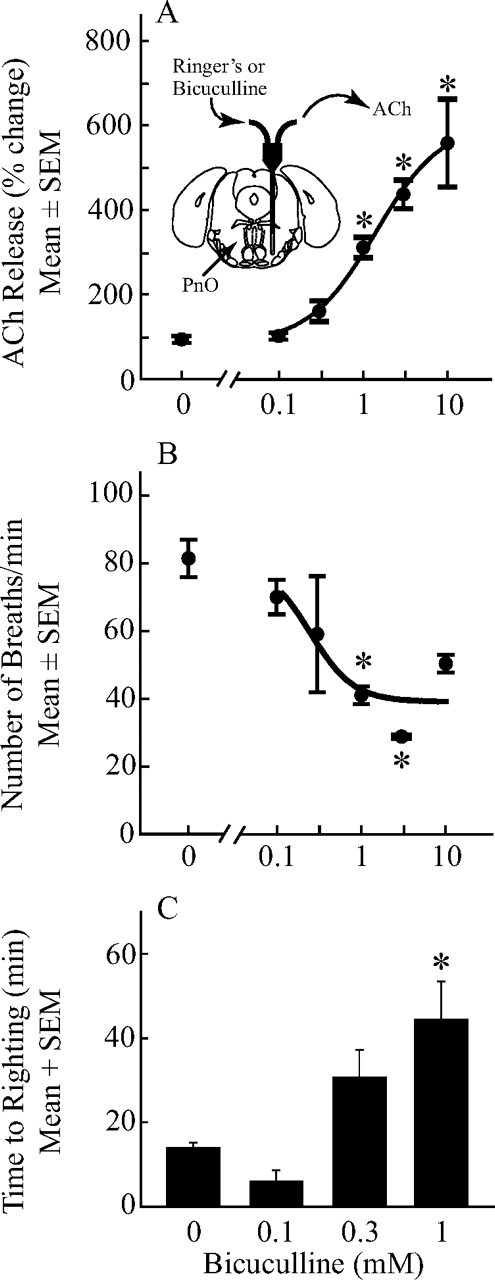
Blocking GABAA receptors in the PnO caused a concentration-dependent change in three phenotypes of wakefulness. Asterisks indicate a significant difference from control (0 mm bicuculline). A, Bicuculline increased ACh release in the PnO. The inset shows a coronal diagram modified from a mouse brain atlas (Paxinos and Franklin, 2001) to schematize a microdialysis probe in the PnO. The probe was perfused with Ringer's solution or Ringer's solution containing one concentration of bicuculline, and acetylcholine (ACh) was collected from the outlet tubing. The dialysis membrane is drawn to scale (1 mm length and 0.24 mm diameter). The concentration of bicuculline accounted for 87% of the variance in ACh release. Data are from three mice per concentration for a total of 18 mice. B, Dialysis administration of bicuculline to the PnO decreased respiratory rate. The concentration of bicuculline accounted for 76% of the variance in rate of breathing. Data are from three mice per concentration, for a total of 18 mice. C, Bicuculline administered to the PnO increased time to righting after cessation of isoflurane delivery. The concentration of bicuculline accounted for 76% of the variance in anesthesia recovery time. Data are from three mice per concentration, for a total of 12 mice. A–C, *p < 0.05, significant difference from control (0 mm bicuculline).
