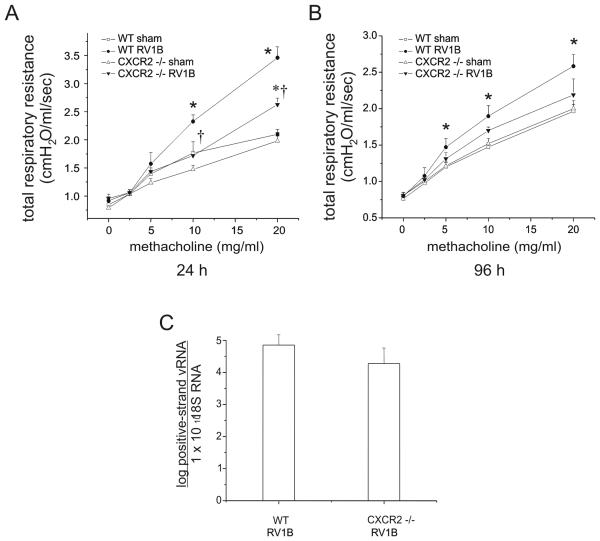
Figure 6.
CXCR2−/− mice show reduced airways cholinergic responsiveness 24 h post-infection. Following anesthesia and endotracheal intubation, changes in respiratory system resistance to nebulized methacholine were measured using the FlexiVent system (Scireq, Montreal, CA). Mice were studied either 24 h (A) or 96 h post-viral exposure (B). (N=5 mice per group. Open squares, sham-treated wild-type mice; closed circles, RV1B-treated wild-type mice; open triangles, sham-treated CXCR2 −/− mice; closed triangles, RV1B-treated CXCR2 −/− mice; error bars represent ±SEM, *different from respective sham group, †different from wild type RV1B-treated group, p<0.05, two-way ANOVA.) C. RV1B-infected CXCR2−/− mice show comparable viral loads compared to RV1B-treated wild type mice 24 h post infection. Wild type and CXCR2−/− mouse lungs were homogenized in Trizol reagent 24 h post exposure. RNA was extracted and analyzed for the presence of positive strand RV RNA. Viral copy number was normalized to the quantity of 18S RNA present in mouse lungs. (N=6 mice per group, bars represent geometric mean±SEM.)