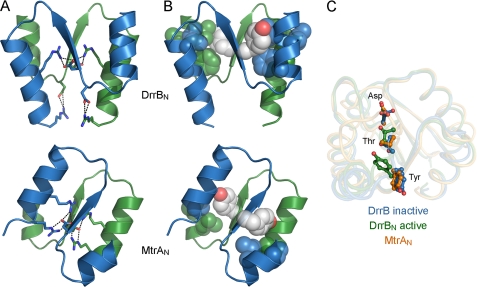
FIGURE 2.
Dimer interfaces of MtrA and BeF3−-activated DrrB receiver domains. A and B, ionic and hydrophobic interactions, respectively, at dimer interfaces. The α4-β5-α5 regions of two protomers (blue and green) are shown as ribbon depictions, with conserved charged residues that participate in intra- and/or intermolecular salt bridges (dashed lines) shown in stick format and hydrophobic residues involved in intermolecular contacts shown in spheres (carbons, blue and green; nitrogens, blue; oxygens, white). Tyr switch residues (white spheres) are oriented away from the interface in DrrB and form the central contact of the interface in MtrA. All dimers are aligned relative to the green protomer, illustrating the ∼50° rotation of the blue protomer around an axis perpendicular to the plane of the interface. C, conserved switch residues in DrrB and MtrA. Asp residues at the site of phosphorylation and conserved Thr and Tyr switch residues in inactive DrrB (blue), active DrrB (green), and MtrA (gold) are displayed on backbone traces of aligned receiver domains. Orientations of the Thr and Tyr residues in MtrA are similar to those observed in inactive receiver domains.