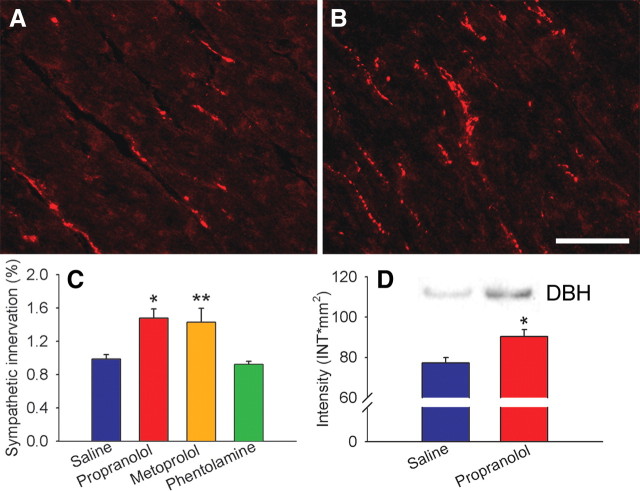
Figure 1.
Adrenergic receptor blockade increases ventricular sympathetic innervation. A, Section of ventricular myocardium from a saline-infused rat showing dopamine β-hydroxylase-immunoreactive sympathetic axons. B, Innervation density appears to be increased after a 7 d infusion of propranolol. C, Quantitative analyses of dopamine β-hydroxylase-immunoreactive innervation expressed as percentage of myocardial field area occupied by stained axons. Relative to saline-infused rats (n = 12), myocardial innervation density was increased by infusions of propranolol (n = 8) and metoprolol (n = 6) but not by phentolamine (n = 4). D, Ventricular tissue from adjacent sections assessed by Western blot shows that propranolol also increases DBH protein levels. Product was analyzed densitometrically and normalized to total protein. Scale bar, 100 μm. Results are presented as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 or **p < 0.01 versus saline.