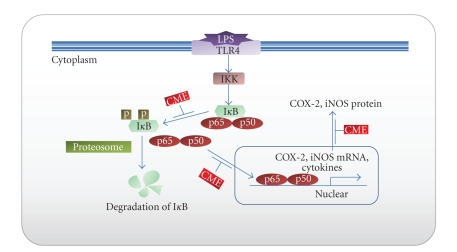
Figure 1.
Main molecular targets of CME that lead to inhibitory effects on LPS-induced inflammation action. CME blocking NF-κB signaling pathway via inhibition of (i) IκB phosphorylation, (ii) subunits (p65/p50) of NF-κB trnaslocation in nuclear, and (iii) proinflammatory mediators (COX-2, iNOS, etc.) transcription. Blue arrows indicate the NF-κB signal pathway and target gene that DNA binding site of NF-κB. Red boxes indicate the inhibition effect of CME. CME: Crude methanol extract of Citrus aurantium L.; IKK: IκB kinase; IκB: Inhibitor of κB in cytoplasm; p50/p65: subunits of NF-κB; COX-2: cyclooxygenase-2; iNOS: inducible nitric oxide synthase.