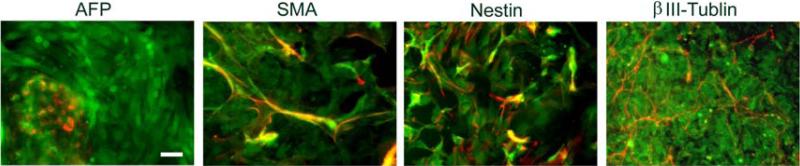
Fig. 4.
In vitro differentiation of BGO1V2-EFG via EB formation. Differentiation of BGOV2-EFG cells was initiated by forming EBs in the absence of MEFs and bFGF. Positive staining for AFP, SMA, nestin and βIII-tublin was identified (red), indicating that BGOV2-EFG cells can differentiate to express markers of ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. Scale bar = 50μm.