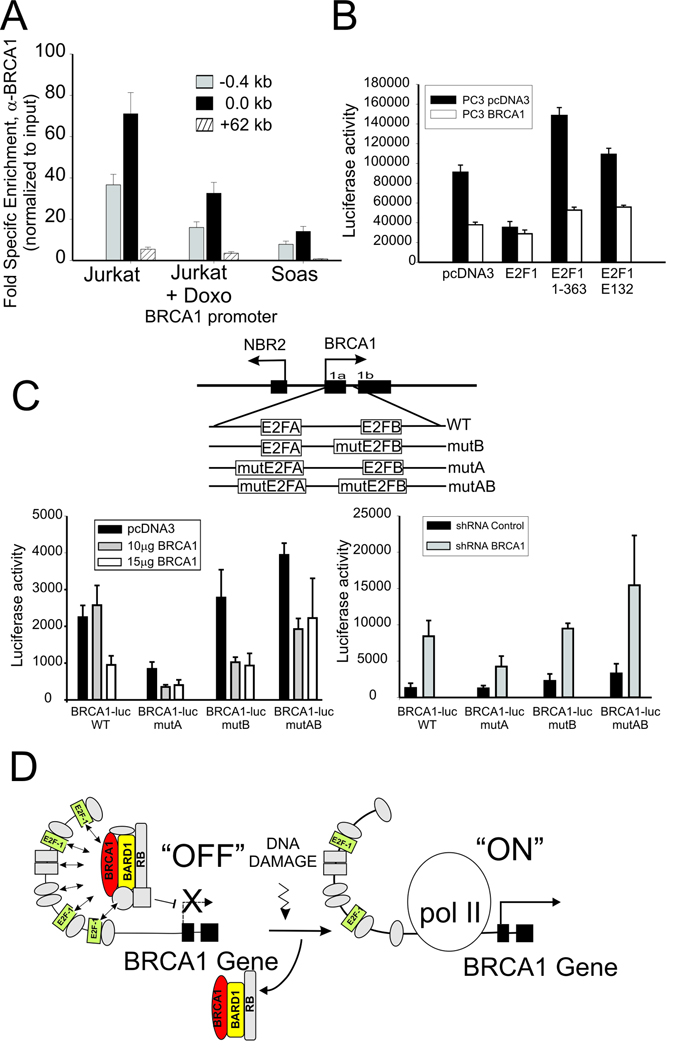
Figure 6. BRCA1 assembles at the BRCA1 promoter in association with E2F-1 and Rb complexes.
(A) BRCA1 enrichment by ChIP at BRCA1 promoter of untreated and Doxorubicin treated Jurkat cells compared to untreated Rb-deficient Saos cells normalized to nonspecific IgG. Error bar indicates standard error and mean from 2 independent experiments. (B) PC3 prostate cancer cells stably over-expressing BRCA1 (PC3 BRCA1) or empty vector (PC3 pcDNA3) were co-transfected with the BRCA1-luc reporter plasmid (pGL12) and wild type or the indicated mutant E2F-1 expression vectors (see text). Error bars show the standard error of the mean from 3 independent transfections. (C) BRCA1 regulation of the BRCA1 promoter depends on the E2F binding sites. BRCA1 was over-expressed (left) or depleted (right) in cells transfected with reporter plasmid containing wild type or mutated E2F transcription factor binding sites within the BRCA1 promoter sequences (see schematic diagram above). Result are the mean and standard error from 3 independent transfections. (D) Hypothetical schematic diagram depicting BRCA1 negative autoregulation by a complex containing BRCA1, E2F-1 and Rb at the BRCA1 promoter, which is up-regulated by displacement/disruption of this complex at the promoter to allow BRCA1 transcription in response to genotoxic stress. Note that E2F-1 complexes are rearranged but not completely lost from the promoter.