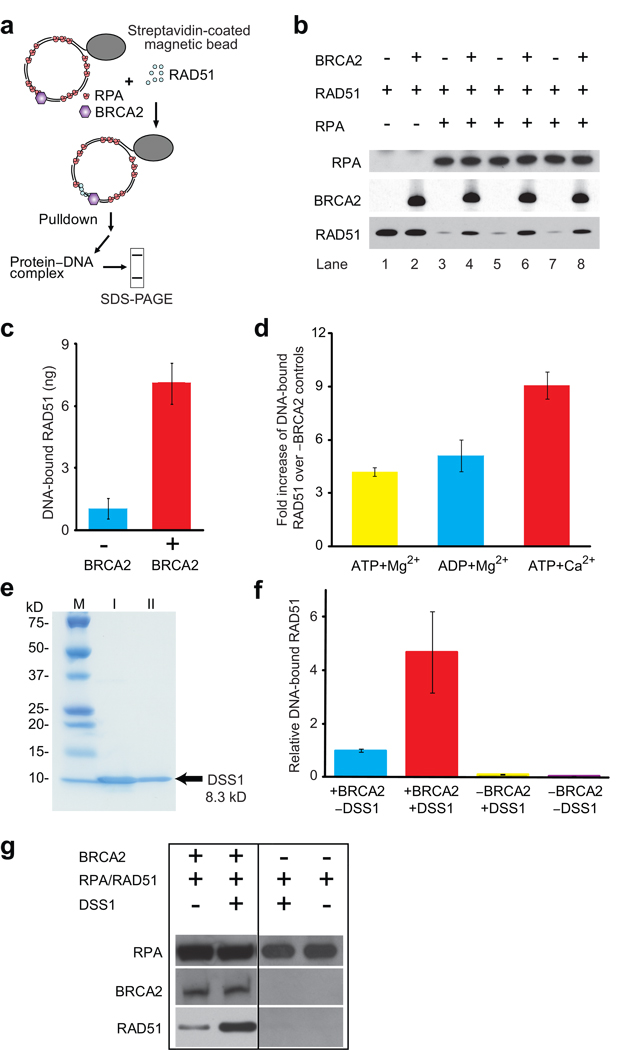
Figure 2. BRCA2 promotes RAD51 binding to RPA-covered gapped DNA.
(a) Assay design. (b) Immunoblots of the proteins bound to immobilized gapped DNA substrates. Reactions contain 0.2 µM (nt concentration) ssDNA, 0 or 20 nM RPA, 13.3 nM RAD51 (1 RAD51 per 15 nucleotides), and 0 or 0.4 nM (25 ng) BRCA2. (c) Quantitation of DNA-bound RAD51 shown in b. (d) Quantitation of DNA-bound RAD51 in the presence of different nucleotide cofactors. BRCA2 was 0.32 nM (20 ng), all other components were as in b. Plotted is fold increase over controls lacking BRCA2. (e) Purification of human DSS1 protein. I, pooled fraction of chitin column eluate. II, pooled fraction of Mono-Q column eluate. (f) Immunoblots of the proteins bound to immobilized gapped DNA substrates. Reaction contained 0.2 µM (nt concentration) ssDNA, 20 nM RPA, 13.3 nM RAD51 (1 RAD51 per 15 nucleotides), 0 or 4 nM DSS1, and 0 or 0.08 nM (5 ng) BRCA2. (g) Quantitation of DNA-bound RAD51 shown in b. Plotted is fold increase over absence of DSS1. Error bars represent s.d. of n=3, and in one case n=2.