Fig. 4.
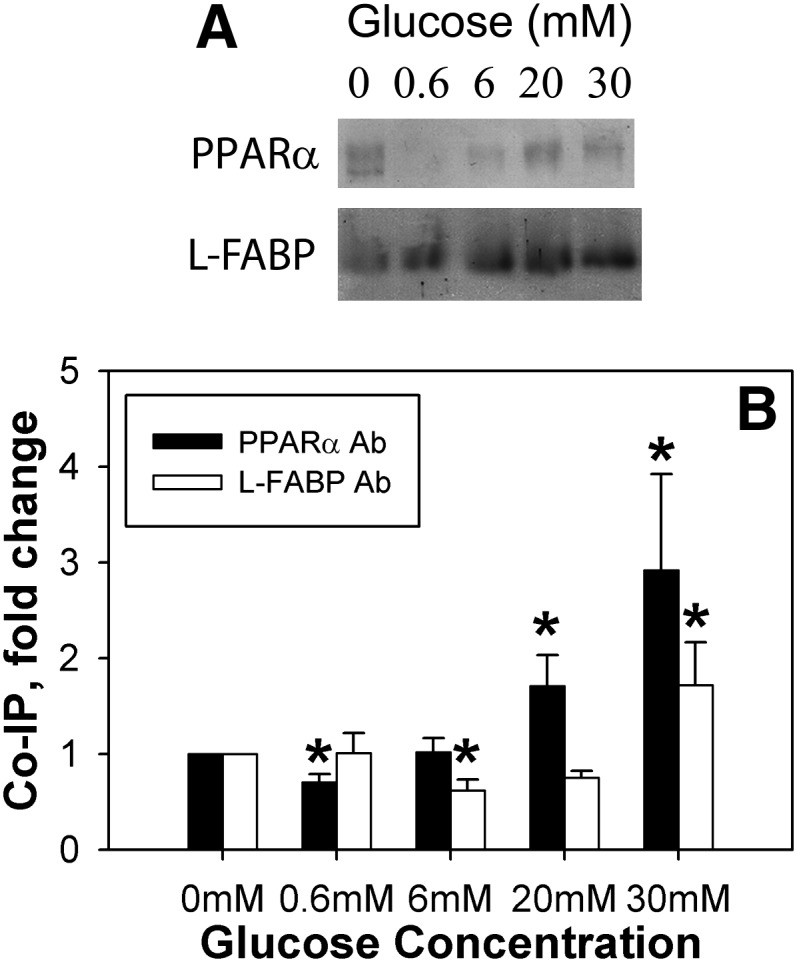
High glucose concentrations increase PPARα and L-FABP co-immunoprecipitation. Equal concentrations of PPARα and L-FABP proteins were mixed in the absence and presence of glucose, and the resultant mixtures were co-immunoprecipitated with the PPARα antibody and assayed for the amount of L-FABP protein (A, L-FABP; B, ▪) or co-immunoprecipitated with the L-FABP antibody and assayed for the amount of PPARα protein (A, PPARα; B, □). A: Representative image of co-immunoprecipitation results for PPARα or L-FABP protein. B: Values are presented as the mean fold change ± SEM compared with the 0 mM glucose controls, n = 4. Asterisks (*) indicate significant differences from the 0 mM controls; P < 0.05. Co-IP, co-immunoprecipitation; L-FABP, liver fatty acid binding protein; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor.
