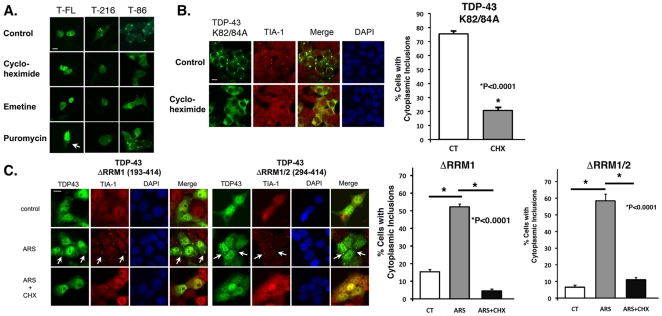
Figure 7. Regulation of TDP-43 inclusion formation by stress granule modulators.
A) The translational inhibitors cycloheximide (50 µg/ml, 1 hr) or emetine (20 µg/ml, 1 hr) disperse inclusions formed by WT-TDP-43::EGFP (T-FL) TDP-4386–414::EGFP (T-86), while puromycin (20 µg/ml, 3 hrs) increases formation of TDP-4386–414::EGFP inclusions formation. Puromycin also induces formation of cytoplasmic inclusions formed by WT and TDP-4386–414::EGFP (arrows). However, puromycin does not change the abundance of TDP-43216–414::EGFP (T-216) inclusions. B) TDP-43::EGFP lacking the nuclear localization signal (TDP-43 K82/84A) forms abundant cytoplasmic inclusions that co-localize with TIA-1 (anti-TIA-1 antibody, red) after arsenite treatment. The inclusions are dispersed by co-treatment with cycloheximide (50 µg/ml, 1 hr). Quantification is shown in the bar graph to the right. C.) Cells were transfected with the TDP-43 ΔRRM1 and ΔRRM1/2 constructs (N-terminal EGFP tag). After 24 hrs the cells were subjected to two conditions: arsenite (0.5 mM, 1 hr) or arsenite plus cycloheximide (50 µg/ml, 1 hr). The cells were then fixed, and immunocytochemistry was performed TDP-43 inclusions co-localized with TIA-1. Arrows point to representative inclusions showing co-localization of TDP-43 and TIA-1. Cytoplasmic TDP-43 inclusion formation was not apparent under basal conditions, however under conditions of arsenite exposure both constructs formed inclusions that co-localized with TIA-1 and were cycloheximide reversible. Quantification is shown in the bar graphs to the right. Scale bar: 10 µm.