Fig. 2.
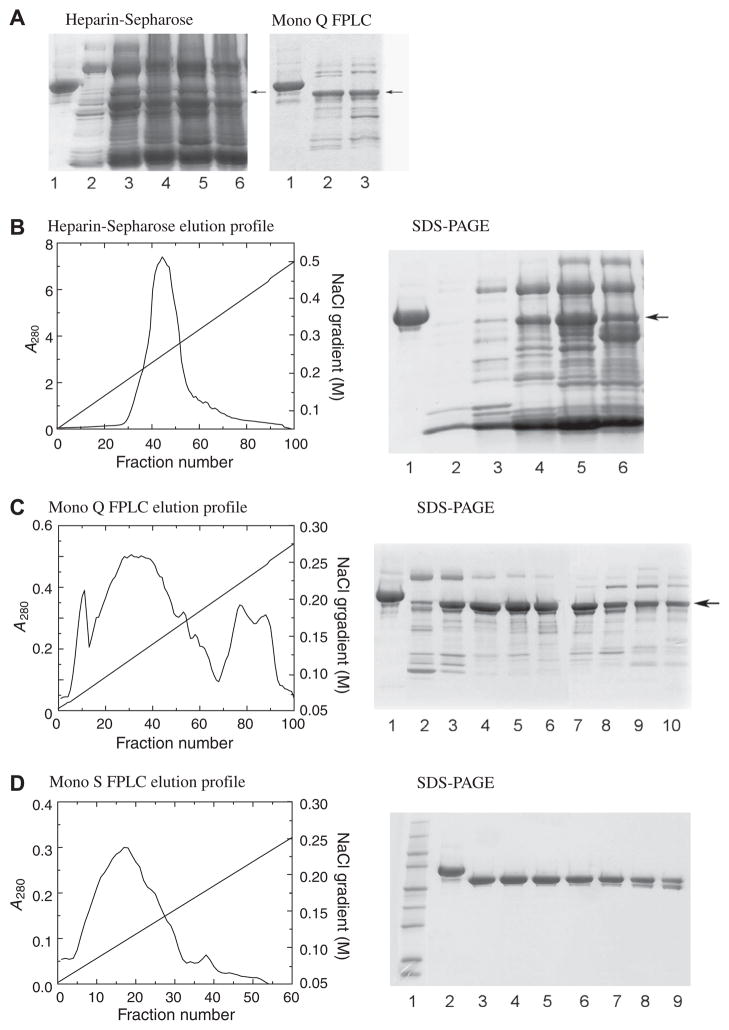
Purification of recombinant HCII. (A) SDS–PAGE of recombinant HCII (active fractions) after partial purification on heparin-Sepharose (left panel) and Mono Q FPLC (right panel) of HCII expressed from a construct with 13 initial mutations, with plasma HCII (lanes 1) as a standard. Arrows indicate the HCII bands. The electrophoretic mobility of recombinant HCII is slightly faster than that of plasma HCII due to the lack of glycosylation. (B) Elution profile on heparin-Sepharose of HCII expressed from the construct containing all silent mutations, and SDS–PAGE of the active fractions (lane 1, plasma HCII; lanes 2–6 are fractions 32, 35, 40, 45, 50). (C) Elution profile of recombinant HCII on a 5 ml Mono Q FPLC column, with SDS–PAGE of active fractions (lane 1, plasma HCII; lanes 2–10 are every 5th fraction, from 20 to 60). (D) Elution profile of recombinant HCII on a 5 ml Mono S FPLC column, with SDS–PAGE of active fractions (lane 1, Mr markers; lane 2, plasma HCII; lanes 3–9 are every 5th fraction, from 10 to 40). A280 values of the fractions were measured in 1 cm cuvettes. The yield of this prep was 14 mg.