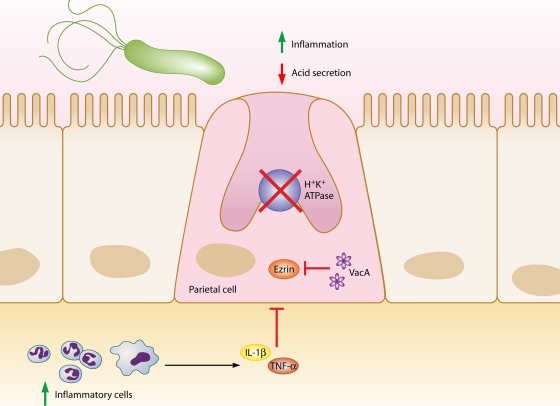
FIG. 2.
Relationships between H. pylori, inflammation, and acid secretion. H. pylori infection can reduce acid secretion and increase inflammation via multiple intermediates. Increased production of IL-1β and TNF-α from inflammatory cells inhibits acid secretion from parietal cells. Acid secretion is also inhibited by repression of H+K+ ATPase α-subunit promoter activity, in addition to VacA-induced proteolysis of ezrin.