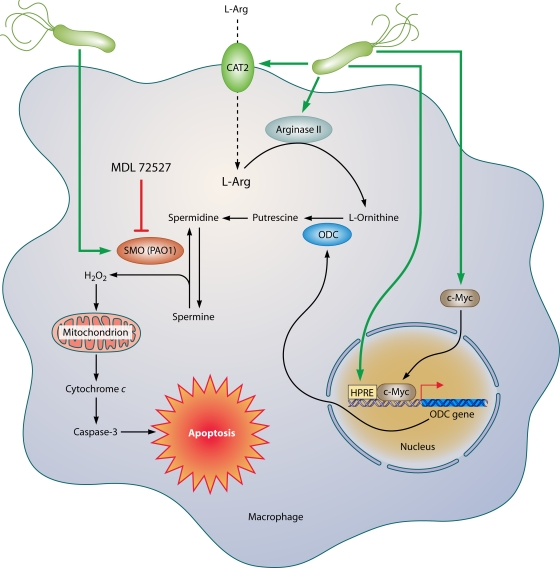
FIG. 4.
Mechanism of macrophage apoptosis caused by H. pylori. This pathway is dependent on the activities of the enzymes arginase II, ODC, and SMO. Induction of arginase II enhances synthesis of l-ornithine, which is converted into polyamines by ODC via a process that requires both H. pylori activation of the ODC promoter and c-Myc as a transcriptional enhancer. Production of the polyamine spermine provides a substrate for SMO, which is also upregulated by H. pylori. SMO generates H2O2, which causes mitochondrial membrane depolarization, cytochrome c release from mitochondria to the cytosol, and caspase-3 activation, followed by apoptosis. Induction of macrophage apoptosis leads to impairment of mucosal immunity to H. pylori, chronic inflammation, and cancer risk (48, 50, 116).