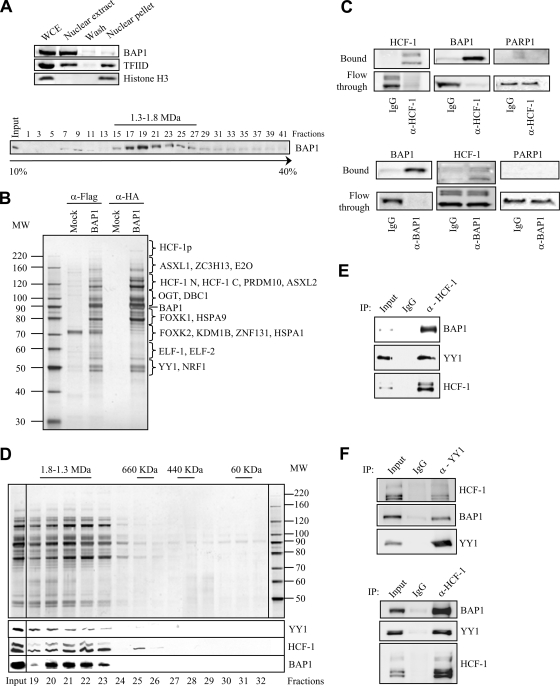
FIG. 1.
BAP1 assembles high-molecular-weight multiprotein complexes containing the YY1 transcription factor. (A) (Top) Extraction of cellular BAP1 protein. HeLa nuclei isolated with hypotonic buffer were extracted with 300 mM KCl for 30 min in order to obtain the nuclear extract and the chromatin/nuclear matrix pellet fractions. The nuclear pellet was washed once. All fractions were resuspended in the same volume and were used for the immunodetection of BAP1. TFIID was detected as a marker for the transcriptional machinery and histone H3 as a marker for chromatin. WCE, whole-cell extract. (Bottom) Endogenous BAP1 migrates in high-molecular-weight fractions. A HeLa nuclear extract was fractionated using glycerol density gradient ultracentrifugation. Fractions collected from the top to the bottom were subsequently used for the immunodetection of BAP1. The gradient was calibrated with the previously purified CtBP complex, whose estimated molecular size is ∼1.3 to 1.5 MDa. (B) Purification of BAP1-associated proteins. A HeLa cell line stably expressing Flag-HA-BAP1 was used for sequential double immunopurification using anti-Flag antibody and anti-HA antibody columns. The Flag- or HA-eluted proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and detected by silver staining. The mock purification was conducted using a stable cell line generated with the empty vector. Several regions were cut from the gel, and the polypeptides were identified by mass spectrometry. MW, molecular weight (in thousands). (C) Immunodepletion of HCF-1 (top) or BAP1 (bottom) from nuclear extracts using an excess of an anti-HCF-1 or anti-BAP1 polyclonal antibody. A nonrelevant anti-HA polyclonal antibody was used as a control IgG. BAP1 and HCF-1 were immunodetected in the beads and the flowthrough fractions. The nuclear protein PARP1 was detected as a negative control. (D) BAP1 forms high-molecular-weight multiprotein complexes. Fractionation of the BAP1-purified material was performed using a Superose 6 HR gel filtration column. The eluted complexes were detected by silver staining. BAP1, HCF-1, and YY1 were detected by immunoblotting. MW, molecular weight (in thousands). (E) Reciprocal immunoprecipitation. The Flag-purified BAP1 material was used as input for additional immunoprecipitations with a polyclonal antibody against HCF-1 or a nonrelevant anti-GFP antibody (IgG control). The immunocomplexes were extensively washed, and YY1, HCF-1, and BAP1 were detected by immunoblotting. (F) Interaction of endogenous HCF-1, BAP1, and YY1. A HeLa nuclear extract was used for immunoprecipitation with a polyclonal antibody against YY1 (top), a polyclonal antibody against HCF-1 (bottom), or a nonrelevant anti-GFP antibody (IgG control). The immunocomplexes were washed, and YY1, HCF-1, and BAP1 were detected by immunoblotting.