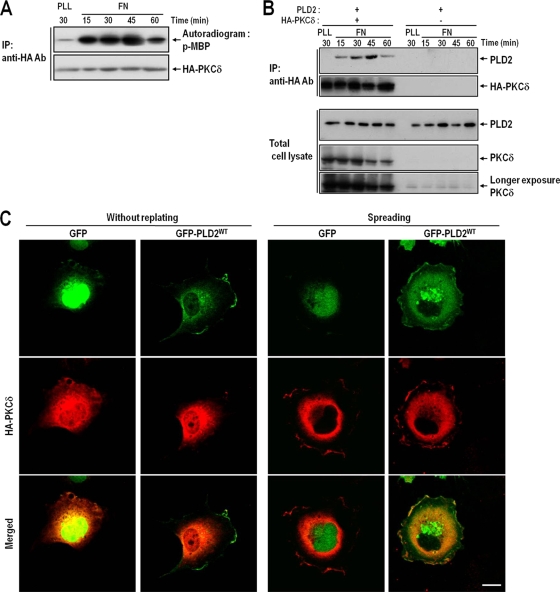
FIG. 2.
The interaction between PKCδ and PLD2 parallels increases in PKCδ activity. (A) COS-7 cells were transfected with HA-tagged PKCδ. One day after transfection, cells were serum starved for 24 h, detached from culture dishes, maintained in suspension for 3 h, and replated on FN for the indicated times (15, 30, 45, or 60 min). “PLL” represents the control and indicates the PKCδ activities of adherent cells on PLL for 30 min. Cells were then harvested; HA-PKCδ was immunoprecipitated (IP); and kinase activities were assayed as described in Materials and Methods. The results shown are representative of three independent experiments. Ab, antibody. (B) COS-7 cells were cotransfected with PLD2 and either HA-PKCδ or a vector control as indicated. After 24 h of transfection, cells were serum starved for 24 h, detached from culture dishes, maintained in suspension for 3 h, and replated on FN for the indicated times (15, 30, 45, or 60 min). “PLL” represents the control and indicates the amount of interaction between PLD2 and PKCδ in adherent cells on PLL at 30 min. Cells were then harvested, and HA-PKCδ was immunoprecipitated with an anti-HA antibody. The immune complex thus obtained was subjected to SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with an anti-pan-PLD or anti-PKCδ antibody. The results shown are representative of three independent experiments. (C) COS-7 cells were cotransfected with HA-PKCδ and either a GFP control vector or wild-type GFP-PLD2 (GFP-PLD2WT), as indicated. Cells were serum starved for 24 h, detached from culture dishes, maintained in suspension for 3 h, and then replated on FN for 30 min. The cells were then fixed and stained with an anti-HA monoclonal antibody in order to detect PKCδ expression. Images are single confocal sections (n = 3). Bars, 20 μm.