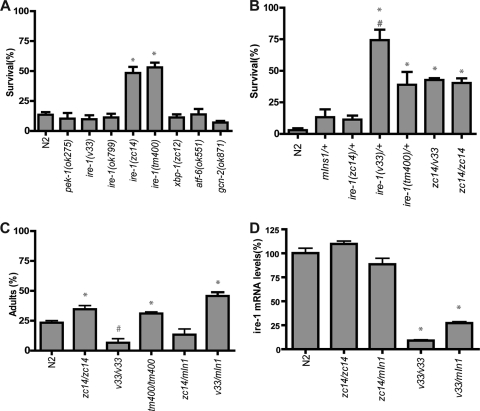
FIG. 5.
Effect of UPR mutants on hypoxic and tunicamycin sensitivity. (A) Animals with the indicated alleles were exposed to hypoxia for 20 h without any pretreatment, and survival was scored after a 24-h recovery (*, P < 0.0001 versus N2 by unpaired t test). (B) Animals with different ire-1 genetic backgrounds were tested for hypoxic survival without any pretreatment. (*, P < 0.001 versus N2; #, P < 0.05 versus zc14/zc14 or zc14/v33, unpaired t test). (C) Animals with different ire-1 genetic backgrounds were tested for sensitivity to Tm toxicity. Eggs were laid on the plates with 1 μg/ml Tm. After 3 days, the percentage of adult worms was scored (*, P < 0.01 for results greater than those for N2; #, P < 0.01 for results less than those for N2, unpaired t test). (D) The levels of ire-1 mRNA from the wild type and mutants were determined by quantitative RT-PCR by using a primer pair annealed 5′ of ire-1 cDNA. {*, P < 0.01, versus N2, zc14/zc14, or zc14/mIn1[dpy-10(e128) mIs14(p-myo-2::GFP)], unpaired t test}.